It is known that the foundation should be selected, based on the characteristics of the soil, landscape features and the mass of the future building. For houses with a rather large weight, there is a separate type of deep downstream foundations. All their design is aimed at dispersing the load and creating a sustainable base. In this article we will talk about choosing and designing deep downstream foundations.
Technology device of the foundation of deep down
The foundation is called a design that serves as a support for the house, which provides excessive pressure on the ground. The main difference of such a foundation lies in its layout to the depth, much greater than that of ordinary or small-brewed. At such a depth, the foundation does not freeze, is not subjected to powered forces and can maintain its sustainability for decades. The essence of such a deep bookmark is that the lower layers of the soil have a higher density than the upper one. For this reason, due to the increased density of the soil, the foundation can withstand extremely heavy structures.
It goes without saying that the bookmark of such a foundation will be very laborious and costly with the financial side: digging a deep trench, a large amount of sand and rubble for drainage, an increased consumption of concrete, which still needs to be seen ... Nuances of the mass, so before work everything is necessary Plan and prepare.
Foundations of deep downstream are used to build multi-storey buildings, shopping centers, industrial facilities and other structures from brick and reinforced concrete elements. The use of such a design is advisable only in areas with a deep level of groundwater. If the water is close to the ground surface, the base laying will not make sense, since you cannot get supports on a dense solid ground.
Classification of foundations of deep down
There are several types of foundations of deep downstream, excellent in shape, a method of building, depth of bookmark, constructive features and materials used. Some species are used to create a solid and durable base for heavy buildings, others allow you to construct a bellged construction with underground rooms, the third reduces horizontal loads on the structure.
Classification of foundations of deep downstream:
- sink wells;
- caissons;
- thin-walled shells;
- drilling supports;
- walls in the ground.
We suggest talking about each of the species in more detail.
Sleep wells
The lowered well is closed and, as a rule, the symmetric design of the cross-type. It is placed in the primer and collected from several sections, after which it is carefully concreted.
Typically, the installation of lower wells is carried out due to the force of their own weight, but in some cases, vibrations are subjected for solid fixation. The main rule is observing the strictest verticality during immersion. As the well is lowered into the ground, the ground from under it is gradually taken out, using a hydraulic installation or a grapple excavator for this purpose.
Highed wells are made from various materials, including reinforced concrete, stone or brickwork, can sometimes use metal and wood. The lower part of the structure is equipped with a cutting part with corners or chapels. It is reinforced more than the whole body of the well. The outer walls can be stepped or vertical with a decreasing diameter to the top.
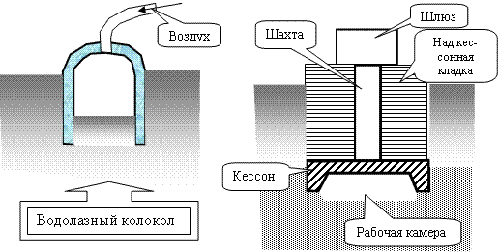
Caissons
Caissons are used in cases where the foundation of deep downstream has to be mounted below the level of groundwater. The caisson is a peculiar chamber with faded air, which dries and pushes soil for development. When the caisson chamber is lowered into the ground, it is poured with concrete mortar.
Cement consists of the following structural elements:
- mine;
- camera;
- compressors;
- gateway devices.
The use of deep downstream caisson foundations is associated with large labor and financial costs. This method is quite complicated in performance, and therefore in modern construction it is practically not used, replacing alternatives.
Thin-walled shells and drilling supports
Thin-walled shells are called hollow metal cylinders, the diameter of which can vary from 3 to 6 m. The length of one section can reach 6-12 m, and if necessary, they increase them, connecting bolts and enhancing fasteners with welding.
To immerse the long metal sections in the ground, use a vibration device. Like lower wells, thin-walled shells in the lower part have knife parts. After installing the elements in a strictly vertical position, internal emptiness is poured with concrete solution.
Drilling supports are similar to thin-walled shells, but made entirely of concrete. They are installed in a pre-drilled vertical mine. The body of the concrete support is reinforced, and in its lower part it makes a small extension. It significantly reduces the load on the dense soil, and also prevents the loosening of supports by the powers and other adverse phenomena.
Wall in soil
Walls in the ground as foundations are erected mainly for the construction of blunting structures. At first, the contour of the building is planned, after which, in accordance with the markup, they dig a narrow and very deep trench (as for a belt foundation, only much deeper). Then this trench is filled with pre-prepared reinforced concrete sections, or poured with concrete solution.
Such a foundation of deep downstream is used to build residential multi-storey buildings with underground parking, transitions, warehouse, working and industrial premises. This method is relevant for densely populated megacities, where developers are forced to fight for each free cubic meter of space. In recent years, houses with underground tiers are growing increasingly in mind their obvious practicality.
Ribbon Foundation Building Technology
Build your own hands the foundation from thin-walled supports or wall in the ground is quite problematic. The easiest way to consider the technology on the example of laying a ribbon foundation of deep downstream. However, before starting, it is necessary to take care of the preparatory work: cleaning the construction site, export of construction waste, place of storage and storage of building materials, etc. Also preparation includes the removal of the upper fertile soil layer with a thickness of 10 to 30 cm. When with all these manipulations, it is completed, you can proceed to markup and earthworks.

The markup of the foundation of a deep downstream is carried out according to the same principle as the marking of the usual belt basement - with the help of stakes and cord. Experts recommend to make marking with two parallel lines, the distance between which denotes the width of the future trench. So you can explicitly submit the location of the future foundation.
Useful advice: After installing the markup, check it with the method of diagonals. Since most rectangular buildings, measure both diagonals of this rectangle and compare them. If they are equal, then the markup is made correctly, and the foundation side is also equal to each other.
Excavation:
- In accordance with the markup, dig the trench of the required depth. If in your case the depth of the foundation laying depends only on the characteristics of the soil, the level of its freezing and the level of groundwater level, determines the width of the base should be guided by the degree of need for high bearing capacity. In other words, the more the mass of the building and the weaker soil, the wider it is necessary to make a ribbon of the foundation.
- To determine the optimal width, make a simple calculation of the carrying capacity of the soil. To do this, find a lot of buildings without a foundation, find out the carrier of the soil, find the size of the soil that can withstand the building without the foundation, find a lot of houses with the foundation and find out, the size of the ground base capable of withstanding such a mass.
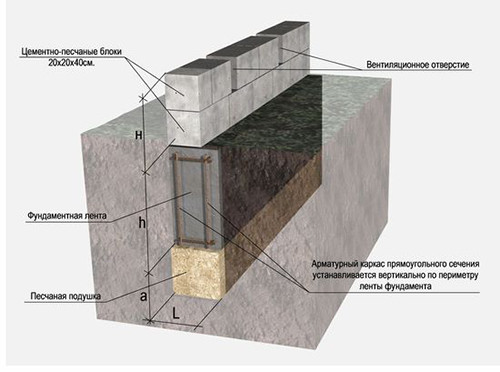
- Install the formwork inside the trench. In the case of conventional tape foundations, formwork can be made with your own hands from unnecessary boards or plywood. However, here work with a completely different scale, so in order to avoid errors, it is recommended to use industrial production shields. Make sure that there are no cracks and lumens between the elements of the formwork, through which the concrete solution could be found.
- Secure the formwork from the outside by slopes and P-shaped brackets. For the manufacture of the latter, you can use steel reinforcement, or lean from wooden plates. Such brackets will not allow the formwork to fall under the inner pressure of the solution.
- To the inner sides of the formwork shields, bring small carnations or thin wooden slats to designate the level to which the concrete solution will be flooded. All marks must be in one horizontal plane, so that the upper edge of the foundation turns out to be smooth.
- At the bottom of the trench, put on a 15 cm of sand, see it, richly watering with water, and then pour 15 cm rubbank and also sink. This drainage pillow will be removed moisture from the concrete part of the foundation.
- Shipping formwork and rubble bottom trench with waterproofing material. It can be a conventional rubberoid or polyethylene construction film with a thickness of 200 microns. Waterproofing not only protects concrete from moisture in the ground, but also will not allow it to spread, and water from the solution to absorb soil. If this happens, the solution will lose elasticity and strength, and after the frost, it will become fragile and collapsed under the weight load of the future building.
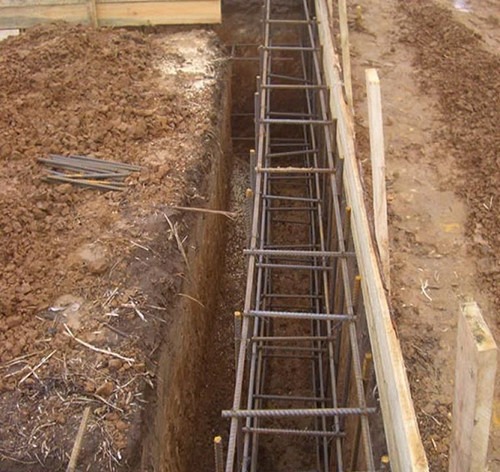

- The next step is reinforced. To do this, you need relief steel bars with a diameter of 12-14 mm. Cut the reinforcement into two belts, fastening the rods with vertical racks. Use steel wire for knitting. Many experts believe that the welded connection of the elements in the construction of foundations is better not to be applied, since the welding reduces the strength of the steel structure.
- The upper and lower belt of the structure is a reinforced mesh in several rods laid parallel to the length of the entire foundation. These rods are fastened by crossings to which, in turn, vertical support racks are occasted. These racks are needed in order to locate the reinforcement frame at the very bottom of the trench, but on some elevation. So after the fill with concrete, the metal core will be protected from the destructive impact of moisture from all sides and can evenly distribute the load. The frame is made on the surface, after which they are lowered into the trench with the help of a crane.
- Now you can proceed to the pouring of concrete. The main complexity here is that it is necessary to pour it right at once, and this is quite a large amount, and without a large technique there is no need to do. If for some reason it is not possible to pour the whole solution at once, you can do it in stages. However, the fill should not be filled with horizontal layers, but vertical. To make it possible, break the foundation to a few segments, separating them to formwork, and each of these segments immediately fill to the top. The bay is one, you can again let the batch of solution and start working with the following, etc.
- Concrete pouring should be performed gradually. After filling 15-20 cm from the trench height, stop and stop the concrete with reinforcement or a park in several places, knock on the outer walls of the formwork. It is necessary in order to release air bubbles that reduce strength. Conduct the procedure every 15-20 cm fill.

- Leave the foundation until complete drying. Depending on weather conditions, it may die from 2 to 4 weeks. So that the atmospheric moisture does not overlook the solution, cover the formwork with polyethylene.
- After drying, do the foundation waterproofing. To do this, remove the formwork and treat the external concrete walls with bitumen mastic, liquid rubber, waterproofing. You can remove the formwork only after 2 weeks from the moment of filling the foundation when the concrete is fixed by 70-80%.
- Measure the horizontal of the top of the foundation. If the differences are observed in height, it is necessary to build a low formwork and pour an aligning cement screed, otherwise the walls of the house will turn apart. If the surface is smooth, it should also be protected by waterproofing material.
- Make a backstage. There remains free space between the walls of the trench and the foundation. It needs to be filled with soil, but you can also use for this sand and rubble, creating additional drainage. The backfill should also be made in stages - every 30-40 cm thoroughly tamper the soil (sand).
Independent work with fundamentals of deep downstream is impossible in view of their large-scale and the need to use heavy construction equipment. In preparation, special attention is paid to calculations to accurately determine the required amount of materials.



















 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...