The wooden architecture of the Scandinavian countries is rationality and natural harmony. Russian huts can be bolded to call the prototype of the Finnish house. However, today the technology of wooden architecture has left far forward.
What is the secret of such popularity?
Finnish house building technology has a number of benefits:
- tree - ecological and grateful material, causes a unique feeling of comfort;
- the walls are paired by a layer of insulation, which, in combination with a natural tree, perfectly isolates from noise and even with critical temperatures in the room dry and warm;
- the construction of such a house takes a much less time than brick, you clearly save on building and interior decoration;
- for the construction of Finnish houses, high-quality timber are used, sharply and fitted and fitted, and the building looks neat and aesthetic.
Stages of design
In pursuit of profit and in the fight against competitors, domestic projectors are started in the development of dwelling in Scandinavian style, but, unfortunately, the exit is obtained by a wooden house of poor quality, overwhelmed with details and far from a given architectural direction.
It is advisable to contact directly into Finnish offices with many years of experience, the benefit of them has long and successfully cooperate with Russian-speaking customers. The manufacturer's chosen by you is obliged to specialize in residential wooden houses, and not in garden verandas and villages. It is desirable that the company will provide a full cycle, and not bought the missing details from different plants: the difference set, the more difficult the fitting and docking of the elements. Do not chase at low price. You build a house in which you may live a few generations of your family.
Right foundation
Theoretically, the house can be built on any foundation, which was previously done. In the process of evolution, concrete and stone options disappeared, leaving two leaders: UCP (insulated Swedish stove) and Uff (insulated Finnish foundation). With the right execution at the final stage of construction of the foundation, you get the finished overlap of the first floor with integrated communications, drainage system, electrical wiring and warm floors.
A decent performer often comes from Finland to make sure that your foundation meets the project requirements and only after that launches delivery for construction.
Material wall
The main thing: the forest should be only winter blanks. Twisted at another time, it is subjected to chemical processing and durability of such a log in doubt. The most qualitative raw material for the design of the Finnish house from the bar – this is the wood of the highest grade "A" from Central Finland. The perfect option is when the slats are glued from homogeneous rocks. Snow-white spruce is considered the most reliable, but capricious in the processing material. Its thermal conductivity is higher than the rest of the breeds. For example, a 20 cm glued timber with a thickness of 20 cm will provide the same heat insulation as a brickwork in 2 m. Houses from pine are called second-rate - over time it darkens, and the bitchs are separated from wood mass. Another applied larch and cedar.
Insulation for Finnish houses
Throughout Europe, including Finns, the basalt mineral wool Rockwool is used for these purposes, which has proven itself well. Basalt is a volcanic rock formation, absolutely not a fuel and even prevents the spread of the fire. In addition, it is a durable, durable, noise absorbing and thermally insulating, it is not terrible for temperature changes.
To insulate horizontal joints along the entire length of the crowns, the vapor-permeable ILLBRUCK ribbon is placed. It shrinks under the weight of the upper layer and, expanding, fills all the free space.
According to the construction standards of Finland, the houses from the glued bar with a thickness of at least 180 cm even in harsh weather conditions do not need insulation. The fact is that the quality of the assembly and docking of the corners are rather responsible for maintaining the temperature, rather than the thickness of the walls.
Natural heat loss goes upstairs through the roof, so special attention should be paid to its design and insulation. The European climate is softer Russian, but there it is customary to put insulation with a thickness of 400 mm, in Russia this is for some reason 150-200 mm.
The windows preferably have an electric heating, as Hatrick does.
Exterior and interior of Finnish houses
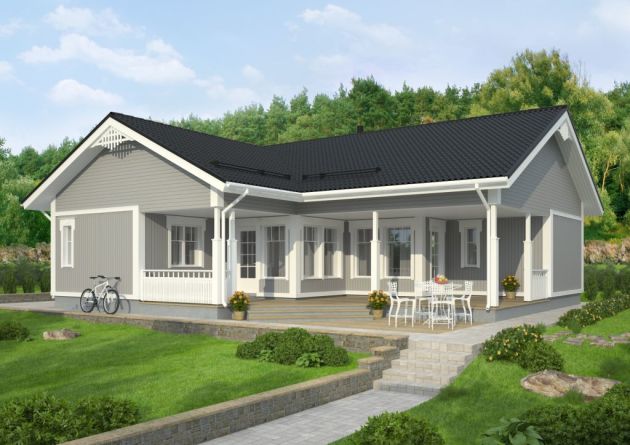
A typical Scandinavian dwelling is distinguished by conciseness, its exquisite simplicity is combined with impeccable performance. Log, devoid of decoration and unnecessary details, one and a half or two floors, it has a double roof so that snow is not stood. On the first floor in front of the entrance door, there is usually a terrace, and above it is a balcony with large windows.
Typical color of the exterior finish of the facade - white, light gray, beige, all natural shades of wood. Separately ease of eaves and platbands.
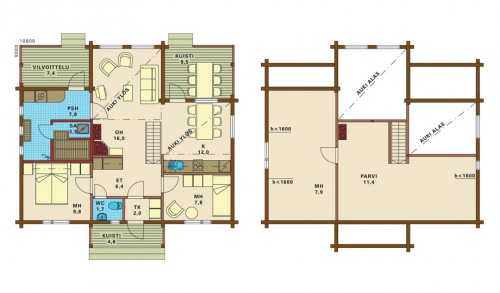
In the house, as a rule, two entrances, each with a separate Tambour, a functional element of heat retention. Entering, we find out in a spacious lounge, which leads to the kitchen, guestroom, office. In the tradition of Finns - to have a large kitchen with a dining table in the middle. On the second floor under the roof slots there is a bedroom. Often there is a sauna in the house. We offer to admire the photo of the interior of the Finnish house.
Varieties of building
Solid Bruz House
After cutting, the tree is sent to the drying to prevent shrinkage in the future. Next, it is profiled and processed the surface before the smoothness of the lining. In the log section there are square or rectangular, with a profile-lock or without it.
Benefits of timber:
- all items are already cut in advance on the calculations and do not require a subgon in place, which facilitates and speeds up assembly;
- of all the species, this is the most environmentally friendly method - there are no glue and resin;
- relatively low cost due to less cost;
- in the case of a profiled wall timber, the walls do not need additional interior decoration.
Disadvantages:
- sweeping, cracking;
- congenital wood defects - fungus, cavity, pests living inside;
- the need for insulation of seams;
- of the non-public timber, it is technologically difficult to drive out a steady wall, and therefore additional backups are needed;
- shrinkage at home is 3-4 cm per meter wall.
Finnish house of glued bar
This technology is based on the ultraying of logs from natural wood to ideal geometric sizes. By processing on special equipment, the bars are increased by mini-spike and glue up to 13 meters in length. It happens another D-shaped form when the inner surface seems folded from BRUSEV, and the external one - from rounded logs. The profile lock is designed so that its spikes are ideally included in the grooves, not letting go there moisture and making the wall extraordinarily durable. Today, this method of building the house is recognized as optimal in Scandinavia and is recommended for the Cold Russian Climate. Combating manufacturers try to use only first-class glue, for example, the Finnish company Kilto, not containing harmful substances.
Advantages:
- the probability of deformation and drying is eliminated;
- the density of the adhesive seam is higher than the density of wood, and this allows you to freely plan overlaps of any length and large-scale rooms;
- at the end of the work, the house is ready for commissioning, time for shrinkage is almost no required.
Disadvantages:
- a higher price is about one and a half times more expensive than a solid timber;
- due to glue, the natural air balance of wood is disturbed, which can entail changes in the microclimate indoor.
Frame Finnish House
There is no clearly established norms for the design of the island, which means that each company is individual. There are only general requirements for the material - it should be a dry strand board; Wooden timber is used extremely rare. This principle of the construction is the most easy-to-year and popular worldwide for more than five hundred years.
Domocomplektoms are:
- Block-modular. For this method, the framework is not required, the house is collected from both cubes. Elements are mounted at the factory and brought into place of construction. This kit already has a finished facade, and sometimes interior decoration. His only drawback is that large dimensions of fragments make it difficult to deliver.
- Panels with a high degree of study. The construction site includes harvested sandwich panels with wooden lamellas, insulation, vapor insulation, doors and windows. In place, all this is assembled on a pre-constructed frame, partitions are put, overlapping and roof are put.
- Only basic panels. The level of readiness is only the outer walls of the wall. Everything else is installed on the spot.
- Pre-sliced \u200b\u200bkit. All the details of the building are already siled in advance at the factory and are numbered according to the project. Materials such as insulation and stove are brought in procurement form. Plus this method is that the house can be built as a constructor with minimal involvement of special equipment.
Technology Building
The construction technology of the frame house allows you to build it with your own hands. If the project is already agreed, then proceed to the foundation. Depending on the weight of the structure and the characteristics of the soil, the columns or screw piles are most often used.
If you have a small house for a middle family, then there will be quite a fairly columnar foundation:
- 120 - 150 columns are harvested.
- At a distance of 80 cm from each other, the ordinary brown is done by a hole with a depth 1 m and a diameter of 20 cm.
- In the resulting recesses insert acquired pipes, and the space around them is filled with rubble and gravel.
- With the help of a funnel, cement is poured into the holes.
The screw principle is also very popular precisely the fact that it is valuable to the use of manual labor. This allows you to strictly monitor the drilling level. It is important to remember that the pile disintegration is categorically prohibited, as the natural dumping of the soil is disturbed.
Stages of the construction of the Finnish house
Draft floor for Finnish house
- Ruberoid is fonded to the coating basis; The perimeter makes a stroke of a bar, which is the basis for the draft floor.
- In increments of about 40 cm, lags made of ugly wood with a cross section of 245 x 100 mm are laid, and the insulation and vaporizolation are inserted between them.
- From above put plywood sheets 18 mm thick. The draft floor is ready.
Walls of the Finnish house
- The board cross section represents a rectangle of 150 x 50 mm. For the reliability of compounds in the bars, the locks are implanted and secured them with self-draws. The design must be mobile, since at first there is a shrinkage at home.
- The frame of each wall is mounted separately on the maximum smooth surface. On each side you need to make bodies that support frame frame.
- After installing in place, the walls are inhabited by boards or in the case of a frame-shield construction, it is sewn with a non-combustible windproof material with a thickness of 25 mm.
- At this stage, all the walls are firmly joined with the lower bar with spills and bolts fasten the angular boards with each other.
Second floor of the Finnish house
- The overlap is made like the first, but it is experiencing smaller loads and allowed to take the beams of 50 mm height.
- The draft floor stood with bars with a step of 35 cm, insulation, put vapor barrier and sew plywood sheets.
- The second level walls are collected similarly to the first.
Roof of the Finnish house
- 150 x 50 mm rafters are attached to the upper bars of the walls of the second floor.
- From the inside of the beam closes plywood, and with an outdoor - wooden crate.
- The cavities between lags are closed with insulation and waterproofing material.
- Roofing material, for example, ceramichell, put on rafters.
At this stage, say that the frame house was still early. Now it needs to be thoroughly insulated inside and outside, insert windows and doors, conduct communication and interior decoration.
Option of external insulation
- On the perimeter of the walls make the crate and the gaps are making mineral wool.
- The second layer is a foam.
- The slots between the sheets of foam are filled with mounting foam.
- The next layer is vaporizolation.
- With the inner, that from the outside between the final coating and the layer of insulation, it is necessary to leave the gaps of 25 mm for the natural circulation of air.
Small but cozy dwelling
Nordic character is calm and loves exquisite simplicity. Many Scandinavians have long been in their homeland for a long time for one-story buildings. Small cottages are another kind of Finnish houses. Here are the facts that they say in their favor:
- With the same area, this housing is much cheaper and its construction will be put in a more compressed duration.
- Finishing or repair work is easier and faster.
- It has been proven that life on the "zero" level brings closers with nature and as if the household is splitting.
- The perfect option for a young family or, on the contrary, the elderly couple, whose children live separately.
A typical project of one-story Finnish house includes everything that: a small living room, one bedroom, kitchen, bathroom and pantry. On average, the total area of \u200b\u200bsuch a cottage is up to 60 m².



















 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...