Rosemary - evergreen shrub with narrow fragrant leaves similar to coniferous needles. The plant is widely known as the fragrant spicy sharp seasoning, which is added to many dishes. But, in addition to its culinary advantages, Rosemary is also a valuable medicinal plant.
Until recently, Rosemary was available only as potted culture or room plant. It turns out that many years of aromatic culture can easily be grown in the garden or in the garden. Exotic shrub is rapidly rooted in open ground and requires a minimum of attention. The most important thing is that every gardener should know - low frost resistance of the plant, and therefore it will be required to have its own shelter for the winter.
The remaining details of the landing and care of rosemary - read in this selection of material.
Rosemary, Botanical Help
- Rosmarin refers to the family of casnotkovy and is a long-term evergreen shrub.
- The name of the genus is interpreted in different ways: in one sources the word "Rosemary" is translated from Greek, as a "balsamic low shrub", according to others, there is a Latin translation denoting "seaside freshness". In fact, and in another case, the interpretation is absolutely true and corresponds to the morphological characteristics and the natural range of shrub growing.
- In the wild form, rosemary is widespread in the territory of the Mediterranean coast, therefore it is often called it - "Mediterranean shrub".
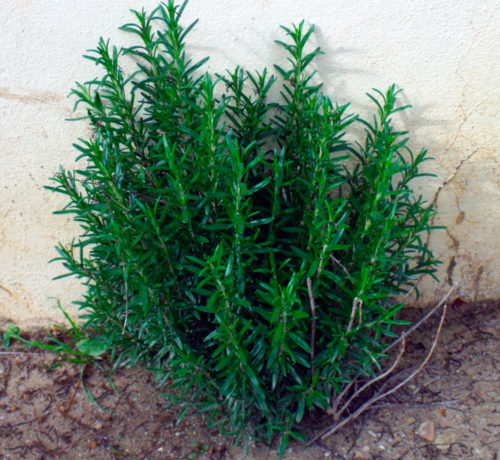
- Rosemary shrub, landed in the open soil, is able to reach height from 50 cm to 2 meters. Young perennial shoots slightly pubescent, tetrahedral, light gray color; Perennial shoots over time are decorated and covered with dark gray sealing bark.
- The root system is powerful and branched, penetrates to a depth of 3-4 meters.
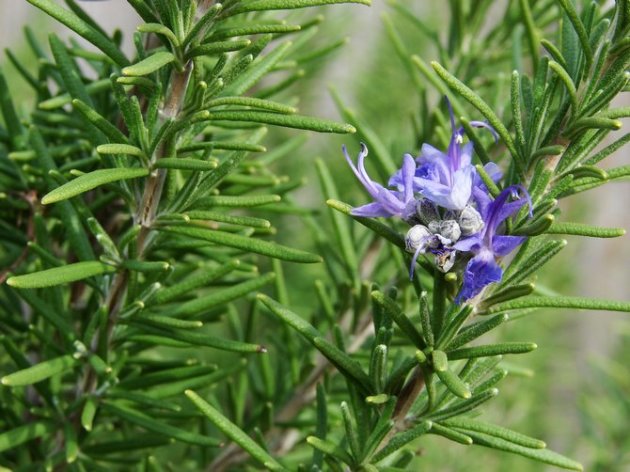
- Leather leaves have a narrowed linear shape, similar to coniferous needles, with opposite seating. From above, rosemary green leaf plate and shiny, bottom - whiten, pubescent. The length of the sheet is 3-4 cm, the width is not more than 4 mm. The main advantage of such needle leaves is their unusual complicated fragrance, resembling sea freshness, mixed with the smell of needles, camphors and lemon.
- Flowers rosemary with small flowers collected in lush buckles. The color of the inflorescence can be different: from white to violet tones.
Rosemary, Plate Features
- Rosemary is a "relative" of such aromatic crops, like lavender, basil, mint, chamber and Melissa. Culture is included in the list of the famous gathering of olive herbs.
- Rosemary has long been famous not only for its spicy, but also healing properties. So, in ancient Greece, students wore wreaths woven from rosemary shoots, and it was believed that the fragrance of the plant improves the memory and helps to concentrate attention.
- In many countries of the Mediterranean coast, Rosemary since ancient times is recognized as a symbol of prosperity, abundance and longevity. That is why at the weddings newlyweds were made to give a branch of fragrant rosemary.
- In the fresh form uses the top young (annual) shoots together with foliage and flowers.
- Rosemary cultivation in open ground is possible only in a soft moderate climate, with warm winter. In cold regions with severe winters, rosemary can be cultured as a room (or container) culture.
- Experienced gardeners learned how to plant rosemary near tomatoes, sweet peppers, cucumbers or potatoes, so that the specific smell of spices scare from the vegetable cultures of insects - pests.
- Other fragrant herbs will also be the best "neighbors" for rosemary: parsley, dill, basil or thyme.
Rosemary, Plant Application
- Thanks to the bright fresh aroma, Rosemary's shoots are widely used in cooking as a spicy sharp seasoning with a light spicy mustard. This is suitable for both fresh and dried parts of the plant. This seasoning is especially common in my homeland, in Mediterranean dishes. The fresh and dried greenery of rosemary is added to the first and second dishes (meat and fish), salads, marinades, drinks and sauces. Rosemary also often insist vinegar.
- Drug type rosemary is a valuable plant and is widely used in medicine. Essential oil containing in rosemary has a bactericidal and wound-healing property. The plant is used as a diuretic and choleretic agent, it can take toxins, normalize the operation of the cardiovascular system, reduce headaches and deal with insomnia. Ramos, infusions and rosemary oils are used in the treatment of impotence, colds, bronchial asthma, rheumatism, Malokrovia, Stomatitis, Furunculose, RAS and ulcers. Ordinary tea with the addition of rosemary sprigs, has a general toning effect on the human body, soothes the nervous system.
- In any case, without consultation with the doctor, it is impossible to independently deal with treatment, as Phyto therapy has its own testimony and contraindications. Like any other strongly smelling plant, rosemary can cause an allergic reaction. With extreme caution, you should use a spicy-sharp seasoning of pregnant women and hypertensive.
- Rosemary's aromatic essential oil is used in cosmetology for treating and improving hair structure. It is rubbed into the skin of the head, add to shampoos or rinsing agents, thereby strengthening the roots of the hair and increasing their delicate. Frequently, the plant oil is recognized as a useful means of rejuvenating effect.
- Evergreen fragrant shrubs are also used for landscape design. Plant, most often, planted with groups or in complex compositions of the mixboarder. In the southern regions, the perennial often serves as a green decoration of fences or walls. And useful phytoncides that highlight the plant enriched and clean the air.
Rosemary in the garden, photo
Rosemary, Capture Secrets
- If the meat dish of pork, rabbit or lamb is putting a sprig of rosemary, the meat will acquire the taste and aroma of this game.
- To prepare a "rosemary paste" you need to mix dry or fresh rosemary leaves with parsley greenery and creamy oil. The aromatic paste is laying under the skin of any poultry (chicken, ducks, turkey) in the field of legs and breasts, after which the meat is baked in the oven or in a frying pan. The dish is extremely tasty and fragrant.
- In the preparation of any dishes, it is impossible to mix rosemary and bay leaf, as these seasonings are not compatible, which will give dishes an unpleasant aftertaste.
- To prepare fragrant "rosemary oil" should be pouring several sprigs of rosemary with olive oil (in a transparent bottle) and insist on the light of about 1.5 months. Finished oil is filtered and overflowing into a dark bottle. Most often, such oil is used as a massage.
- For the preparation of "rosemary" you will need several branches of fragrant seasoning, which is added to a bottle with white dry wine. Drink insist 10 days in a cool place. The finished wine is transfused into a dark bottle and are used inward (no more than 100 g daily) for the general strengthening of the body.
- Very easy to prepare useful "rosemary tea". For this, one teaspoon of dry rosemary leaves is poured with a glass of boiling water and insist about 15-20 minutes. Rosemary tea will be an excellent tonic and strengthening agent, especially after transferring a cold or influenza. And if you add another Melissa, St. John's wort and blueberry leaves - it turns out an effective antidepressant.
Rosemary varieties and varieties
In the culture there are about 5 types of rosemary, of which the most common and in demand is the type of "Rosemary Drug" (often found called "Rosemary ordinary").
- As for varietal diversity, such varieties of rosemary of ordinary have proven best of all: "tenderness", "Rosinka", "Vishnyakovsky Semko", "Severn SEA" (a low grade, reaching a height of no more than 50 cm), "Benendon Blue" ( Compact shape of a shrub with arcoids), "Tassen Blue" (low-layer form of rosemary, reaching no more than 50 cm), "Roseus" (pink color flowers), "Albiflorus" (white color inflorescences).
- Another kind of rosemary of the medicinal is a fluttering subspecies with the name "Prostratus". Often, this subspecies refer to as "Rosemary prostrate." In the height, the shrub reaches from 15 cm to 50 cm, widely (up to 1.5 m) rushing along the surface of the soil. Thanks to its morphological features, the plant is often used in gardening as a soil industry. The most popular varieties of the flutter rosemary are: "Corsica Prostratus" and "Ventsano Prostratus" (creeping and slow-growing shrubs with blue flowers).
Landing Rosemary
Growing rosemary in the garden or in the garden has long been not considered to be exotic. The plant perfectly adapted to our climatic conditions and needs to comply with the main agrotechnical techniques, both when landing and care.
The first time Rosemary will bloom for the second year after landing.
Standings of Rosemary
- Light and thermal-loving rosemary prefers an open sunny terrain (better from the south side of the site), protected from gusty winds and drafts. It is important to know that the lack of light leads to a decrease in the content of essential oil in the leaves of the plant.
- If rosemary landing is carried out in the region with a cold winter, it is necessary to immediately take care of the building of the greenhouse or a greenhouse.
- Rosemary is planted on the bed late in the spring, when completely passes the threat of return freezers, since even a slight decrease in temperature can become destructive for the plant. The same deadlines are followed to set a container with rosemary after wintering indoors.
- The soil for rosemary should be light and loose. In nature, the culture grows on dry sandy and stony soils. Heavy dense or too moistened soils rosemary does not tolerate. Therefore, by defining a place to land a perennial, do not choose a low-rise, flooded terrain and sections with close grounding water. Otherwise, the roots of the plant begin to refine and rosemary dies.
- In addition, an important value for rosemary has a pH level of soil, since in an acidic medium the plant ceases to develop and without a liming procedure may die. The optimal option is a weakly alkaline or neutral soil.
Agrotechnology landing Rosemary
- Landing of any plant involves the presets of the soil: looser (if the plot was drunk), weeds are removed, mineral or organic (humid, compost) fertilizer is introduced and rake.
- For the landing of the "overseas" shrub, it is necessary to take care of the preparation of the soil mixture in advance. To do this, it should be mixed in equal proportions of leafy earth, sand and peat. On 1 bucket of such a loose substrate add another 10 tbsp. Ground chalk (or lime) to ensure a decrease in the level of soil acidity.
- After the soil substrate is ready, you can proceed to the preparation of landing pit. To do this, it is enough to dig a small well, a depth of 20-30 cm, and a diameter of 2 times more (40-60 cm).
- Rosemary seedlock is placed in a moistened pit and fall asleep prepared soil, constantly sealing soil so that emptiness is not formed. After planting, the propelled circle is abundantly watered with warm water.
- Experienced gardeners recommend covering the young rosemary seedling with a plastic film for 4-5 days. Such a reception allows the plant to adapt faster in a new place and better to root. After the specified period, the shelter is removed.
- Young rosemary bushes are planted with an interval of about 50-100 cm from each other.
Rosemary care
Rosemary - a light and drought-resistant spiced culture, perfectly proven itself as a rigorous and rather unpretentious plant. The only drawback of perennials is low frost resistance.
Consider the basic rules for the care of the Mediterranean Shrub.
Watering and loosening rosemary
- Rosemary perfectly tolerate short-term drought periods, but for active growth and development of a young seedling requires regular soil moistening.
- At the same time, it is important that the soil remains moistened, without water stagnation, which is fraught with foliage of foliage and planting the plant.
- The lack of moisture is manifested in the yellowing of rosemary foliage.
- Watering water is best used to use resistant, soft.
- After irrigated the soil around the shrub loose, weeds are removed.
- It is advisable to climb a bed with rosemary with small sand, which will prevent the development of weary grass, and will also increase the temperature of the soil.
Up. rosemary
- Rosemary feeds not often, and if the fertilizer has already been added when landing into the ground, - in the first year, the feeders are not at all necessary.
- As a rule, in the cultivation of rosemary in open soil, the spring makes nitrogen complexes that contribute to the growth and development of green mass. In the fall, shrubs are watered with phosphorus-containing fertilizers.
- Such a scheme for making nutrient elements allows you to get powerful, healthy and densely fruitful rosemary shoots.
- In the spring-summer period, the organic can also be used as a fertilizer, for example, a cowber solution (diluted in water 1: 5). The content in this fertilizer of potassium, nitrogen and other useful trace elements can significantly improve the qualitative and structural composition of the soil.
Fighting diseases and pests of rosemary
- Due to the large content of aromatic esters, rosemary bush is absolutely resistant to pests. In addition, insects avoid "visit" and nearby areas for rosemary, which often use gardens when planning all landings.
- Occasionally, a web mite can appear on the shrub, easily exterminated with special insecticides.
- Rosemary disease is also not scary. The plant has high resistant to various kinds, fungal or infectious diseases.
- Interesting is the fact that room rosemary is less resistant to fungal infections and can "be hurt", for example, malicious dew. The cause of the disease, as a rule, lies in the improper leaving of the plant.
Rosemary trimming
- To the rosemary shrub looks neatly, lush and beautiful, it should be cut periodically. Pruning not only forms the correct crown of the plant, but also contributes to the development of new perennial shoots.
- For this, in the spring, before starting active growing growth, cut damaged, dry or too thickened shoots.
- Every 7-10 years, when the shrubs begin to take off the stems, the plant is rejuvenated and cut off all shoots to the soil level.
- In the summer, Rosmary's shoots are cut to use them as fragrant seasoning for cooking. You can also periodically pinch the tops of rosemary, improving the degree of shrub branching.
- In the fall, the collection and harvesting of rosemary greenery for the winter is carried out.
Preparation for Winter Rosemary
- In order for the thermal-loving plant without problems overlooking the street, it is important to prepare for this period in advance.
- Some flower products \\ gardeners do not risk leaving a spicy culture in the open ground and dig it to transplant in flower pots (or other containers) and put into the room. In the spring, after successful wintering, Rosemary is planted again in open ground.
- In a moderate climate, you can leave rosemary to winter outdoors. At the same time, it is better to cover the multi-fiber (or to build a mini-greenhouse from polyethylene), and the roots fall asleep with sawdust, straw or dry foliage.
- It is also popular with such a method of insulation as "tent". For its construction, the branches of the napnika, in-depth in the ground and located in a circle, are around rosemary. Dry leaves or sawdust inside this tent.
- In the southern regions where frosts do not fall below -10 0C, the plant does not need any shelter and painlessly winter outdoors.
Harvesting Rosemary
- Green rosemary is collected throughout the season, but the massive harvest falls on the autumn period.
- Collect the harvest, namely, cut off the sprigs of rosemary greenery, follows in quiet sunny weather. Young leaves, which grow on the tops of rosemary shoots, contain the greatest amount of essential oil and have a reinforced aroma.
- Cut shoots (can be dried in a dark dry place together with flowers). It is believed that the most fragrant twigs will be those that are assembled before the start of flowering. Dry rosemary sprigs can be additionally crushed or left in original form.
- Rosemary should be dried naturally, without using an oven or microwave oven. In this case, the plant fully retains its unique bitter-spicy fragrance.
- Store dried rosemary in a glass hermetic jar or fabric bag.
Reproduction of Rosemary
Rosemary can be multiplied in different ways: seeds, cuttings, tanks or division of the bush.
propagation by cuttings
- Rosemary is often propagated by means of apical cuttings. Especially a lot of cuttings appears after spring pruning shrubs.
- Cuttings cut approximately 10 cm in length, is removed and perpetuate the lower leaves (at an angle of 45 0) In the loose soil under the film. Depth of seal cuttings - about 5 cm.
- For the construction of mini-teplichke can also use glass or plastic bottles.
- The distance between the cuttings must be at least 8-10 cm.
- In a warm room, with regular moisture and airing the mini-greenhouse, cuttings take root quickly and can be used for planting in open ground.
seed propagation
- This method of propagation is the most time-consuming and laborious, particularly common in regions with a cold climate.
- Seeds can be collected either by yourself or buy at a garden store.
- Before planting the seeds should fill the water for a few hours, so they swelled and were able to grow faster. Some gardeners prefer to germinate the seeds in moist gauze (3-4 days).
- Sow the seeds in February or early March (for 8-12 weeks before the onset of warm weather) in loose fertile soil substrate (you can also use sand or vermiculite).
- Seeding depth - about 3-4 mm.
- The temperature in the room where the container with the seeds should be at least + 20-250WITH.
- Capacity covered with glass or plastic film, provided its regular airing. If the film is to make a few holes - ventilation is not necessary.
- Watering should be moderate, with no stagnation of water (from a spray).
- Seedlings appear not evenly, and as soon sprout a greater number of seeds (1.5-2 months) - shelter with planting container is removed.During this period, it is important to ensure good coverage of seedlings.
- After about a month of rosemary seedlings are transplanted into individual containers for growing.
- In May - June, pre-hardened seedlings are planted in open ground at intervals between instances of 20-50 cm.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
- This method of propagation is the most simple and not time consuming; often used when growing room shape rosemary.
- You simply divide the adult bushes of rosemary into pieces (with roots), each of which is planted separately.
- For a better rooting roots can be dipped in rosemary growth stimulant solution.
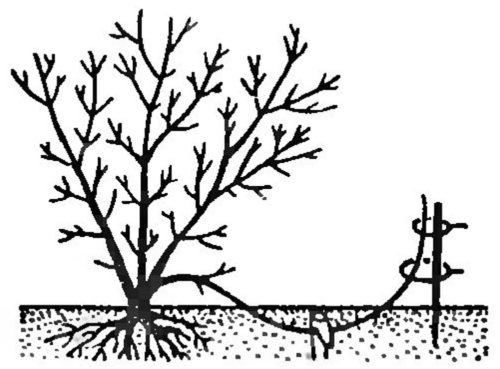
reproduction by layering
- Reproduction by layering involves rooting the shoots lower bushes of rosemary.
- For these purposes, the lowest rosemary escape is tilted to the ground and fix, for example, a wooden (or metallic) bracket.
- All the escape is sprinkled with soil, leaving only his top.
- Regular moistening and after its top will grow further, separated the escape from the maternal bush.
- Escape with the roots formed on it landed at a permanent place.
Thus, evergreen and fragrant shrub, rosemary, can be easily raised on its site. The main condition for the successful cultivation of spiced culture is to comply with the key rules of agrotechnology. Moderate watering, feeding, trimming and shelter for the winter period, are the main conditions for the proper care of rosemary. And for this, the Mediterranean shrub will give its owners year-round seasoning and fresh fragrant greens.












































 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...