Siberia, as you know, a harsh edge, but the family lovers are not stopping such "little things." And indeed, the cultivation in the Siberian region of frost-resistant varieties of roses is no longer surprised. Naturally, the Siberian rose requires increased attention from the flower plant, the knowledge of agricultural landing and plant care features in these climatic conditions. How to successfully grow the varieties of Siberian roses - read in this selection of material.
Siberian Roses Collection: What to choose a variety?
A sharply continental climate of Siberia with short transition (spring and autumn) seasons, requires the selection of the most frost-resistant varieties of roses. Consider what the best roses are suitable for growing in the open ground of the region of Russia.
- Despite the fact that the climatic conditions within the entire region of Siberia are somewhat different from the south to the north, it is worth purchasing Siberian roses seedlings derived mainly in local nurseries. Only such, zoned varieties, have the maximum degree of survival and will be best adapted to the Siberian weather conditions of the harsh winter, late spring and short summer.
- In addition to local copies, Canadian varieties of roses are suitable for Siberia, also adapted to difficult climatic conditions. The main thing when buying roses saplings is to be confident in the truly Canadian origin of the plant, since recently there are often cheap falsification in the colors market.
- And the last option is the grafted varieties of roses, where an unpretentious and endless rosehip is used as a flow. Such varieties of roses are very popular among Siberia flower products.
Basic groups of Siberian roses
Among the huge species diversity of the popular flower, the most suitable groups of roses for Siberia can be distinguished:
- Park roses include wild rose hips and cultural forms of roses with semi-world and non-novice inflorescences. This group refers to highly frost-resistant plants that do not need winter shelter. Park roses are well transferring trimming, while there are capable of forming powerful strong bushes or high hedges.
- Tea roses are considered less winter-hardy, are grown only by grafted on horseback, successfully used on the cut.
- Removable roses are capable of re-blossom and have high frost resistance. Plants form high bushes with long, suitable for cutting, blooms.
- Tea-hybrid roses - a frost-resistant group, which appeared as a result of crossing tea and removable roses. Roses of various colors, bloom until the end of autumn.
- Polyanth roses are represented by strong tight low bushes, no more than 40 cm high. Inflorescences are collected in numerous fine-flowered panicles, continuing blossoms to the most frosts.
- Roses "Floribund" - one of the most popular hybrid groups, are distinguished by beautiful spectacular flowering. Inflorescences are collected in the brush of 20-30 pcs., Blossoms are long (to frost).
- Roses "Grandiflora" are characterized by larger (in comparison with the previous group) flowers, but with fewer buds in the brushes. Plants of this group are considered one of the most frost-resistant and life-friendly roses for Siberia.
- Pleet roses are a curly group, as a rule, neachful roses with an average winter hardiness, need winter shelter.

Best Siberian Roses
The following varieties of roses are considered the most popular for cultivation in Siberia:
- Rosa Sibirskaya, Rosarium Ueesen variety.
The variety is characterized by reusable blossoms, frost resistance and immunity to fungal diseases. The bush is tall, reaches a height of 3rd, is characterized by increased wind resistance. Color color - Purple pink shades.
- Rose Sibirskaya, Sort "Westerland".
An unpretentious plant is distinguished by abundant and spectacular flowering. High bush (up to 2 m), terry flowers, apricot shades.
- Rose Sibirskaya, "New Dawn" grade.
Frost-resistant unpretentious curly variety, blossoms long, throughout the warm season. Orange-salmon flowers color, inflorescences diameter - up to 10 cm. As part of a variety, there are varieties characterized by one-time flowering.
- Rose Sibirskaya, variety "William Shakespeare 2000".
The average (up to 1 m) multi-color variety is highly resistant to infectious diseases. Inflorescences - velvet, bright red color, fragrant. A bush forms a large fluffy brush of inflorescences that hold over 2 weeks.
- Rosa Sibirskaya, Golden Celebration variety.
A grade with a rapid growth rate, an adult bush reaches a height of not more than 1.5 m. Copper yellow shades flowers, with fruit aroma.
- Rose Sibirskaya, grade "chippendale".
The grade reaches a height of up to 120 cm, orange flowers, terry.
In addition to the above, such varieties of roses are popular in Siberia as: "Burgund" (tea-hybrid variety), Amadeus, LLSE Krohn Superior, John Cabot, "Leonardo Da Vinci", "MidSummer", "Lions Rose", "Aspirin" (Roses of the Floribund variety).

Siberian Rose, where to buy?
Cheap Siberian roses are usually represented by seedlings with an open root system, grafted on an ordinary rose hips. Grafted roses, in addition to attractive prices, have increased winter hardiness and immunity to a number of diseases.
Only dug-free seedlings (with an open root system) are subject to rapid transportation and landing in the ground. If you plan a long way to the upcoming place of landing, it is better to buy seedlings in a container (with closed roots), because Even half an hour outdoors can become disastrous for the roots of a young rose.
Canadian roses varieties are quite more expensive, and often flowerflowers face a fake, which does not have anything to do with the real variety of roses from Canada. In this regard, Roses may simply do not fit in Siberia, or they will be far from external signs, as was originally planned when purchasing.
Buy seedlings follow in local nurseries (as already noted above). Basically, the seedlings of Siberian roses are presented:
- rapidly 6-7-year-old bushes (with horse riding),
- annual eyepiece (roses, grafted by the volatilization method),
- currency one-year-old young plants.
Buying rose saplings for growing in greenhouse, naturally, the requirements will not be such strict, but variety varieties are much wider.
Siberian rose, landing features
Successful cultivation of Siberian roses directly depends on the place that is properly selected for the plant for planting, composition and structure of the soil and competent planting of the seedling.

Place and time landing of Siberian roses
- In Siberia, the best time for landing roses - spring, when completely passes the threat of return freezers and the soil warms up to +10 0C. As a rule, landing roses begin in the second half of May.
- If roses saplings were acquired in the fall, it is better to fuck them until spring in the cellar. Autumn landing often end the failure and frozen of a young rapid seedling.
- A landing place is better to choose a sunny, but protected from drafts or strong winds. Given the difficult Siberian climate, the optimally acceptable place for roses will be with the southern side of the garden plot, protected by a wall of any structure or living hedge. As for the open area, in the hot season of the year, the sun's sun rays can "burn" the plant, so roses landed in a light half (under the editorial trees or near the hedge) will be able to bloom longer and more effectively.
- If there are hills on the site (and protected from winds) - it is worth choosing them for planting roses. In such places, the soil freezes less, the water is not stuffed, the plant develops faster and less susceptible to rot.
- The best primer for roses - thin or tuber nutritious (well-fertilized) soil with a weakly acidic (or neutral) medium reaction. In the case of increased acidity, a neutralizer is added to the soil, for example, wood ash.
Agrotechnology landing of Siberian roses
- A pit for planting roses is prepared in advance, it is best in autumn. The land plot is drunk, after which it is directly proceeding to the landing pit.
- The size of the pit is not very large corresponding to the average sizes of the root seedlock. Usually, it is enough to dig 40x40 cm.
- At the bottom of the landing pit, a drainage layer of broken brick or rubble is stacked. From above drainage, organic fertilizers are poured: compost, wood ashes or overwhelmed manure.
- In the spring, the prepared pit is slightly cleaned, shed water and pour out an earthen hormick. If the seedlock is directly immersed in the "Organics", young roots may be damaged and "burn".
- Before landing, long shoots of seedlings are cut. This rule concerns only the grafted varieties of roses, and the vaccination after landing should "look" to the east. Correspondence seedlings before planting are not cut.
- As for the roots, they are better to suck them in the clay "Boltushka" (clay and korovyan in the ratio of 2: 1), which improves the survival rate of the roots. Too long roots (more than 20 cm) can be shortened. Some flowers prefer to grind roots for a few hours in the root formation stimulator, which also contributes to the best suspicion and rooting of the seedling.
- A small holmik from the soil is poured in the landing pit, on which the seedlove is exhibited. Rooting the roots, the plant falls asleep so that the root neck (or vaccination) was below the soil level by 5-6 cm. Pleet roses deepen two times more, 12-13 cm.
- Soil for planting take loose and nutritious, approximately in this ratio:
- clay (part 1);
- sand (1 part);
- peat (2 parts);
- humus (3 parts);
- wood ash (0.5 part).

- Completing the soil after planting, the plant is watered with water, dips the ground (15 cm height) and mulch the rolling circle by humus or sawdust. In the summer, as the seedling increases, the land of the land is gradually cleaned.
- The distance between the plants depends on the variety: for the average, it is sufficient to retreat 50-60 cm, the interval will be needed for empty stronger instances, at least in 1 m.


Siberian Rose, Plant Care
Growing a rose in Siberia, it is important not only to choose enough winter-hardy grade, but also to provide the plant to the right departure during the season. Watering, loosening, feeding, trimming and shelter for the winter are the main agrotechnical activities of roses cultivation.

Watering and loosening of roses by Siberian
- Watering is moderate, abundant, without moisture. Excessive humidification or soil fever provokes root rotting and the development of fungal diseases.
- The norm and frequency of irrigation depend on weather conditions: in the hot period, it is watered 1-2 times a week, the rainy weather is stopped.
- Water under the bush (not falling on the foliage), so that the soil is impregnated about 50 cm. One bruster of roses is required, on average, 10-20 liters of water.
- Frequent watering with small portions is unfavorable for the plant, as it provokes the formation of surface roots, easily damaged in winter.
- At the end of summer, the watering stops, and in the fall (in October) when preparing for winter, the soil is abundantly moisturized.
- After irrigation, the soil is loosened, and when the wild ripples appears - they cut as deep as possible.

Making fertilizers and feeding roses Siberian
- Watering, as a rule, combine with liquid feeding. For these purposes, the infusion of a cowboy is prepared (1:10), chicken litter (1:20) or used ready-made nutritious feeders ("Baikal", "Plata", "rich", etc.).
- In the first year after landing, natural organic fertilizers will be suitable. In the future, 5-6 seasonal feeding per year, alternating mineral and organic fertilizers:
- The first feeding is carried out in spring (before the dissolution of the leaves), after sanitary trimming. Used ammonium nithe or urea solution (1 tbsp. On 10 liters of water).
- After 2-3 weeks, nitrogen-containing feeding, stimulating the growth and development of green masses, repeat.
- During the bootonization period, the third feeding is carried out. Diverse mineral complexes ("Agrikola for roses", "Kemira", etc.) are used.
- Before the start of flowering, a feeding is carried out, for example, a cowbank solution. You can take a ready-made balanced complex ("Gumat", "Baikal Em", etc.).
- After the first flowering (in July-August), the fifth feeding is carried out by any mineral complex.
- The latter feeding (at the end of summer) consists of a mixture of superphosphate and a potassium salt.
- With cold, rainy weather, good results gives an extraxanle spraying of the plant, because Roots during this period has a low level of suction. Extra-corner feeder has a positive effect on the overall condition of the plant, the abundance of flowering and inflorescence.
- During any, "disturbing" plant, events (trimming, transplantation) or deterioration of weather conditions, it is useful to spray roses with a stimulating preparation "Epin Extra".
- In the summer, an active vegetation period, nitrogen-containing fertilizers prevail in the feeding; From August - Potash and phosphorus-containing complexes that contribute to the shrub obsession.
Fighting diseases and pests of roses Siberian
- The most common diseases of roses are black spot and mildew. When defeated by spotty, the leaves of roses are covered with stains, after which they dry and fall. The appearance of a whitic laid testifies to infection with malievable dew. Usually, this disease provokes cool rainy weather.
- If the first signs of the fungal disease appeared on the roses (spots, a bunk) - the bush is treated with any fungicidal preparation ("Phytosporin", "Profit" "Topaz" and others).
- In the fight against insect pests (for example, Tli), insecticidal preparations, such as Aktellik, Intavir, etc. will be needed.

Trimming roses Siberian
- Rose trimming in Siberia is best spent in the spring, since the autumn trimming is fraught with the consequences: it is possible to frozen strongly cropped shoots, slicing infection and a decrease in the total resistance of the plant in the winter stress period.
- In the fall, preparatory trimming is allowed before the shelter of rose bushes for the winter. At the same time, green fat shoots or unbearable tops, buds and flowers are removed, after which the bushes are slightly dipped.
- In the spring, pruning is carried out after complete thawing of soil and final warming. As a rule, this period falls on May month.
- With sanitary trimming, broken, dry, damaged shoots are removed. In addition, trimmed branches growing inside the bush in order to prevent uncontrolled plant thickening. Ideally, an adult rose bush should have about 5 skeletal shoots.
- The varieties of removable roses bloom on the shoots of last year's growth, so they are cut off not much, no more than 20 cm.

Winter shelter Siberian rose
- Preparation for the winter period is one of the most important agrotechnical events when growing roses in Siberia.

- For the winter, bushes of roses (even frost-resistant varieties) can be insulated with different ways, depending on the height of the bush and the specific region of Siberia. Preparatory work is carried out, as a rule, 2 weeks before the upcoming frosts. The main rule is to use dry shelter, as the moisture is the root cause of rose damage in winter. For the same reason, rose shelter activities are carried out in dry weather.
- Snow shelter. Suitable for regions where a large amount of snow falls. In the fall, roses bushes are plunged and sprinkled with sawdust, and in winter - a thick layer of snow. Under the snow cover, it is possible to maintain a stable temperature to the thaws itself. Some flower products are afraid to sprinkle a bushes of roses with sawdust, since with sharp fluctuations in the temperature regime, they can snatch and allocate unnecessary moisture.
- Shelter with a sweetheart. In the fall, roses bushes plunge on a height of about 30 cm, the shoots spray with copper vitrios and are covered with splashes.
- Shelter with cardboard and film. Cardboard boxes are also used as a covering material roses in winter. So that the cardboard does not twist, the construction is covered with a plastic film. Instead of cardboard, you can build a wooden frame, which is "tightened" by any observer material.
- Shelter by spunbond and Loutrasil. For these underfloor materials, a frame or metal (plastic) arcs are prepared, stretch the film from above, capturing a part of the earth around the bush. The edges of the film are sprinkled with soil. Before the onset of strong frosts, the shelter should be all the time, so that the plant is not sick.



- An important point is also the timely and competent "output" of the Rosary after the winter. Already in March, with bushes slightly remove snow cover, leaving a small hollyk until thaw. In April, it is important, periodically, to ventilate bushes, opening a husknik or another design. At the end of April or in early May, the shelter is completely removed. It is better to do it in cloudy weather so that the rose bush is "burned." Moreover, the base of the bush should remain covered until mid-June, when completely passes the threat of return freezers.
- In the spring, after removing the shelter, it is recommended to shed the soil with a special biostimulator ("epic") so that the plant is easier to recover after wintering.

So, the cultivation of roses in Siberia and the care of them is a sufficiently troublesome case, but it is worth it, because the beauty and fragrance of the Queen of Flowers will be able to please households from spring to the most frosts.
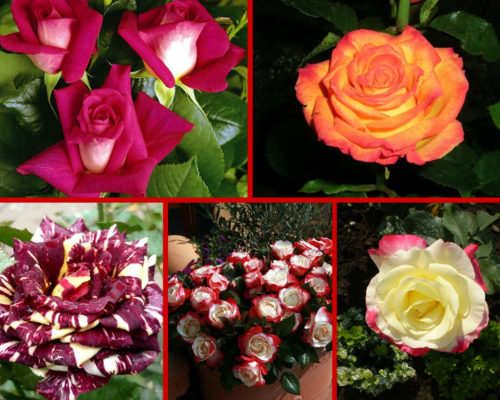
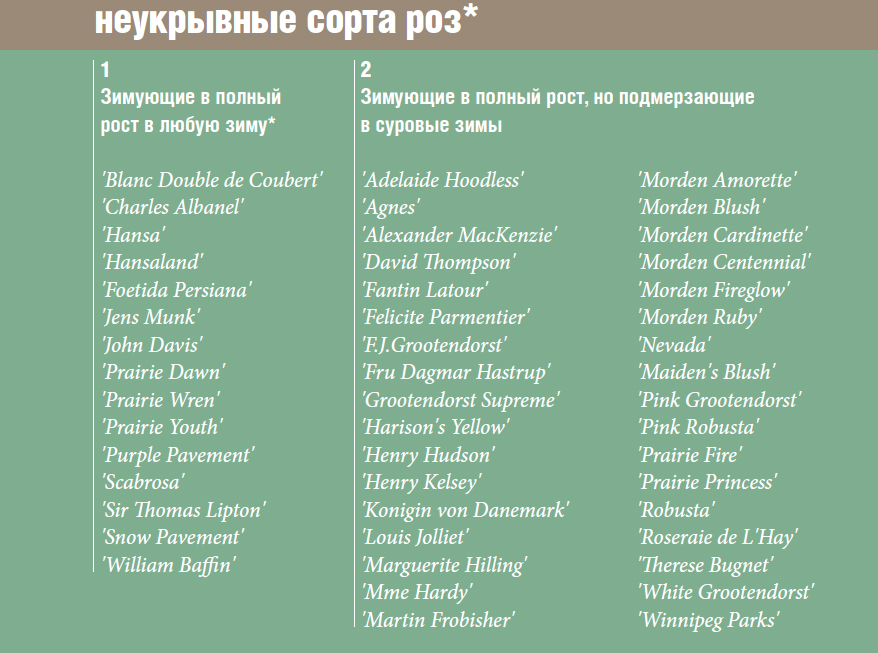
Siberian rose, photo
























 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...