Peony is one of the most beautiful, and therefore popular garden flowers. Large leaves and annual lush flowering will not leave indifferent even the most demanding gardener. Everyone wants to have such beauty on its plot, but despite the widespread prevalence of peonies, they are not so easy to grow them. It is necessary to know certain rules for care and reproduction so that the plants are healthy and beautiful. Here you will find detailed information about peonies in the open soil.
General information about peonies
Flowers Peonies are very good by themselves and are represented in the widest color palette, and therefore they are actively used in landscape design. Plants successfully look both separate large arrays and as a supplement to flower beds and chains. The lowest varieties are often used to decorate alpinarias, and the average and high plant around the trees and along the edges of the lawns.
Peonies are distinguished not only by color buds, but also sizes. They are grassy, \u200b\u200btree and shrub. All of them have a powerful indigenous system of a bump-shaped form, from which several stems with a tremendous or unpaired peristrane leaves of a wide variety of shades, ranging from classic green, ending with dark purple. On each stem dissolves on one bud, and the flower is 15-20 cm in diameter.
The cultivation of peonies will not deliver trouble, if timely produce feeding and prevent the appearance of diseases and pests. These are rather unpretentious plants that are valued and beginners, and professional gardeners are also for the fact that after withering the lush thickets please the eyes until the middle of the autumn. Another advantage of peonies is the ability to grow long in one place (several decades). It is not surprising that breeders are so interested in this plant - the beautiful aesthetic characteristics of a couple with enviable for flowers have created a fertile soil for more than 5,000 varieties.
Types and varieties of peonies
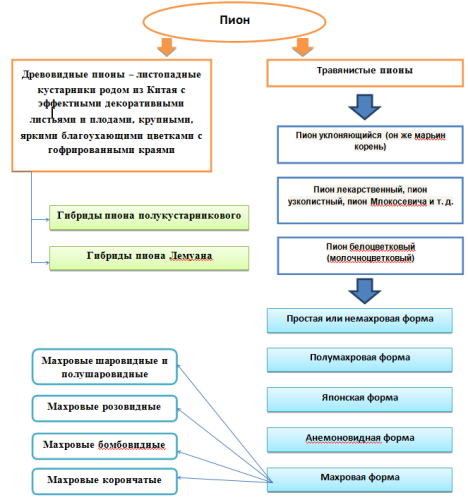
All of now known varieties of peonies are derived from several species of this plant - mostly milky-flux and medicinal. The main difference between the varieties consists in the form of flowers and the "progenitor" - the grade from which he was derived. I will open a small secret: almost all the varieties of garden peonies are obtained from a breast-colored type. This complex hierarchy is clearly demonstrated in the diagram:
Tree peonies
The tree or semi-staple peonies reach 150-200 cm in height and are presented mainly by Chinese varieties.
They in turn can be classified in three groups:
- European - peonies with large terry flowers of the most different color, ranging from a gentle pink, ending with the color of the fuchsia. For this group, large dense leaves and noticeable terrain are characteristic.

- Japanese - peonies with less large buds, but also terry or semi-marched. Their distinctive feature is frost resistance. This is explained by a special way of shilling when the cuttings are vaccinated to the roots of grassy peonies. It is not worth saying that for Russia, Japanese peonies are fit perfectly.

- Hybrid - semi-staple peonies obtained as a result of crossing the peony yellow and done. You can learn them on a saturated yellow color and bright purple specks at the base of petals. On one high escape, 3-4 buds are growing, which are blooming with a diameter of 4-10 cm.

All tree peonies love well-lit sections without drafts, drained and saturated with organic and minerals of the soil. However, even frost-resistant Japanese varieties for the winter are recommended to cover the huskiens and wooden shields.
It is also worth mentioning the hybrid peonies of the ITO obtained from herbaceous and semi-student species. They are distinguished by incredibly lush flowering and unusual color, high resistance to frost, diseases and pests.
Herbatous peions
Herbatous peonies are distinguished by stability to adverse climatic manifestations than helping hard hybrid varieties. These plants are completely unpretentious, however, most of them are flowing at the middle of summer, so if you decide to stop on them, plan a few varieties with different flowering periods.
Popular varieties of grassy peony:
- Escape - a plant with thick vertical stems, reaching from 40 to 100 cm. On each stem is blooming on a single flower with a diameter of about 13 cm of bright pink. The flowering period lasts from the end of May at the beginning of June. The evasive peony is also known as Maryn root and has not only decorative, but also medicinal qualities.

- Medicinal - plant height of 40-90 cm with long root. Initially, the peony was grown only for medicinal purposes, but his decorative qualities across time advanced it up on the "career ladder", and today the drug peony is grown to decorate, sometimes not suspecting his useful side. You can find it on large dark red boots without smell, which bloom in the first days of June.

- Nickname - Landscape designers love to decorate the flower beds, broken down on arid slopes. Peony flowers brightly raspberry in late May. Small flowers are only 6-8 cm in diameter.

- PION MLKOKOSEVICH - the variety is the name of his discoverer. It is characterized by a saturated yellow color, as well as the SIZO-Green foliage and pinkish long stems. Large flowers with a diameter of up to 12 cm are dissolved at the end of May or early June.

White-color peonies
White-color peonies are many varietal varieties and are very popular with gardeners because of their lush flowering and large buds.
Sort of white-color peonies:
- Simple - a separate variety of nonachhrovaya peonies with wide petals of 1-2 rows with numerous pestles and stamens in the center. Flowers themselves are very large and often with corrugated petals.

- Polish - "Light" version of terry colors with petals located in 3-7 rows with a large number of stamens placed between petals or concentric circles. There are several varieties of semi-world peonies depending on the color of the flowers: "Miss America" \u200b\u200bof white color, "Citeria" of the Pink, "En Berry Kazens" coral, "Lasterce" of the Red and "Seblock" burgundy with blacknage tide.

- Japanese is perhaps the most popular view of the petals in 1-2 rows framing the core of the bud. Modified stamens are long narrow petals of the two-color coloring color: from above to the tone of petals, below lighter and yellow. The most popular varieties can be attributed to the "pearl axle" with pale-pink flowers and yellow stamens, the Rannetic "Velma Atkinson" with bright pink flowers, Karara with large boots with a diameter of 16 cm, Berrington Bell with even larger 21- Santimeter buds of bright red and "hot choklet" ("hot chocolate") with dark burgundy flowers and "gilded" modified stamens.

Terry peonies
The terry peonies are particularly popular for a long time and, unlike modest Japanese varieties, a spherical shape of buds with a large number of petals is characterized. They bloom they are incredibly magnificent and beautiful, and the petals, increasing, form several tiers. At the same time, the upper and lower tiers of the same color, and the average is slightly different, which gives the flower even more volume and beauty.
Types of terry peonies:
- Coronated - for them is characterized by a three-tiered flower structure. Popular grade "Raverie Sanda" with pink flowers of 19 cm in diameter with a creamy-yellow middle row of petals. Stems often do not withstand the weights of large flowers, so they are recommended to be tied to supports.

Another sort of crown of peony - "Top Brass" with pinkish flowers and a central bright yellow petals bed. - Spherical and hemispherical - Peonies with horizontal broad petals and narrow at the edges of these pieces. flowers shaped like a hemisphere, and after the disclosure of - scope. Among the best varieties include "Pink Cameo" with flowers of 17 cm in diameter, "Monsieur Jules Elie 'bud 20 cm pinkish-purple color," Alexandre Dumas' lilac-pink buds up to 15 cm and 'Red Charm' with large buds to 22 cm deep red color.

- Rozovidnye - view so named because the blooming buds is very reminiscent of roses. These peonies are characterized by large broad rounded petals. Among the most popular varieties can be distinguished early-flowering "Henry Bokstos" with bright red buds of 16 cm in diameter, late "Solandzh" with large cream-colored buds that can break the stalks, if they do not tie up, "Mrs. Roosevelt" with large pink flowers 23cm diameter.

- Polurozovidnye - very similar to the above, but with an abundance of stamens in the center of the flower. The most interesting varieties: "Goody" bright crimson, "Illini Bella" in the form of a compact spreading shrub with bright red flowers 16 cm in diameter and early-flowering "Beys" with pink buds in 19 cm 3 pieces on each stem.
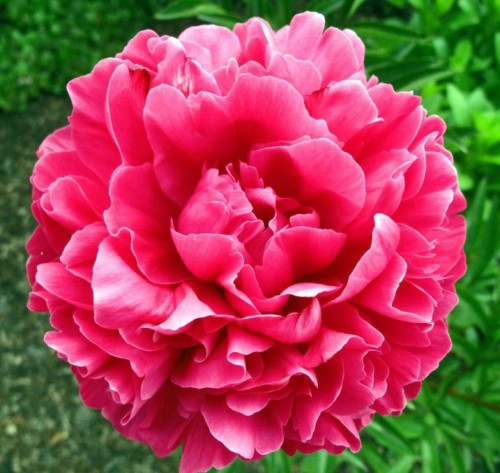

pions description does not give the slightest opportunity and think that it's a mediocre garden culture. They allow you to quench your thirst for beauty, become the object of collectors and just take a leisure helpful and pleasant troubles.
Growing peonies
Breeding peonies like horticultural crops began in ancient China over 2000 years ago during the Han Dynasty. The flower was named in honor of the famous healer Pean, who saved the legends in the battles of life, not only people, but also the gods. Today, the gardens are grown mainly herbaceous peonies, some of whom kept their medicinal properties.
reproduction of pions
Seed propagated pions can manner cuttings and dividing the bush. Seed method is more intuitive and easy for beginners, but unfortunately, it does not allow the plants to maintain varietal characteristics. For this reason, it is used mostly by experienced breeders, so for the "domestic" breeding better to use vegetative reproduction.
In addition, peonies seedlings grown from seeds are developing much longer and blooms much later (for 4-5 years after landing) than those were separated from the maternal bush. However, if you want to try to withdraw your own sort of peony, you can experiment and sow freshly placed seeds at the end of August - they will warm up the next year.
The reproduction of cuttings is much more efficient and more reliable - the plant will retain the varietal characteristics. To do this, it is necessary to separate the small part of the root, on which there is at least 2-3 sleeping kidneys. It is necessary to do it in July, after which it is immediately planted to put in the ground so that by September the plant is rooted. However, such shoots are developing quite slowly and bloomed in 4-5 years, but it is possible to be confident in their quality, especially if we are talking about a rare variety.
Pion landing
Landing and care for peonies does not take away a lot of strength or time, of course, if you do everything right. The first thing to start is to choose a suitable area in the garden. Peeons will have to grow on it several decades, and during this time their root system will deepen in the ground for almost a meter, so they need to transplant them as less as possible. Look for a light platform where the sun shines at least 4-5 hours in the morning. It is better if it is fenced with low shrubs or another obstacle so that the flowers do not suffer from drafts. You should not plant them in lowland so that the water is not stored and did not provoke the root.
Planting peonies to open soil should be engaged in late summer or early autumn:
- A few days before, prepare the pits with a diameter and a depth of about 60 cm, placing them in the meter from each other.
- At the bottom of the holes, pour 10-20 cm of large river sand, crumbs or rubble for drainage.
- On top of the drainage pillow, pour feeding from a mixture of compost, 100 g of dolomite flour, 200 g of superphosphate, 300 g of ashes and 70 g of potassium sulphate. In total, the thickness of such a subtype should be 20-30 cm.
- The remaining space fill in the soil mixed with the compost.
- When the time of landing of peonies come, the land into the pits will noticeably devourge and will be lost, so they can be placed on the rhizomes, sprinkle with fresh ground and slightly to strove so that the seedlings stood smoothly. Do not block the roots too deep - the peonies do not like this!
- Place the first kidney at 3-4 cm under the ground and prepare for the fact that in the first year after rooting the plants will look like stacks, but then it will bloom with all pomp. If the next year they do not bloom, but the bush will look healthy, it means it just has not yet reached the right age.

The transplant of old plants to a new place is also better to carry out in the fall, but remember that the less transplanted peonies, the better - yet it is a strong stress for the plant. The first 4-5 years after landing the flower should not touch at all.
In the spring, no manipulation with peonies is not recommended, but any in life happens, so sometimes you have to make exceptions. By and large, the spring landing does not differ from autumn, but it should be borne in mind that such plants will bloom only for the next year. Provide a good care, "delicious" feeding, and then the result will justify the expectations.
Pion care
If you do not plan to engage in the reproduction of peonies, care is reduced only to watering, feeding and pruning. Food leaves and stalks certainly need to cut immediately and burn so that they do not turn into a source of distribution of diseases, and in the case of peony, it is better to warn better than to treat, but a little later. The remains of the cropped plants need to spray wood ash, spending 2-3 clips on 1 bush.
We rarely water peonies, but abundantly - about 2-3 buckets per 1 adult plant. Water should be leaked to the very tips of the roots to a depth of about 70-100 cm. Special attention to watering should be paid at the beginning of spring, during the intensive growth and formation of buds. After each watering, always slightly loose the soil around the plants and regularly destroy all weeds.
Useful advice: During irrigation, try to direct water directly under the plant, and not on the leaves, otherwise they may turn.
When the snow completely melts, treat the ground around peonies with a solution of potassium mangartage, soluble for every 10 liters of water 2-3 g of chemical (portion for 2 adult bushes). When the shoots are growing, adopt their ammonium nitrate, diluing 15 g in 10 liters of water. In the second half of May, young bushes are about once every 3-4 weeks, water from the top of the watering can with a fine silica with mineral fertilizer and washing powder (1 tbsp. L. 10 liters). Powder in this case will not give the mineral solution to roll from the leaves.
Always feed peonies after sunset or in cloudy weather. When buds begin to appear and in the period of flowering, make more minerals in the soil: Mix 10 g of superphosphate with 5 g of potash salt and 7 g of ate, after which dissolve everything in 10 liters of water and paint the ground around the bushes.
After flowering, the feeding should stop, but continue to water the plants and loose the soil around. It should also be regularly removed to remove stalks and burn them. In August, the kidneys are laid for the next year, so that the future "harvest" will depend on the departure at this time. But when the leaves and stalks begin to be frown, gradually cutting watering to a minimum. With the onset of the first frost cut the ground part of the plants almost to the earth itself. Fresh-lost peonies should be covered with a peat mulch or sawdust with a layer of 7-10 cm to insulate for the winter. In the spring, mulch should be deleted. Old bushes age from 3 years for winter can not be covered - they will survive cold without any problems.
Peony diseases
The most formidable enemy for colors are viral diseases, and in 90% of cases they appear due to poor-quality planting material. But even if you are seedlings of peonies in a proven nursery with a good reputation, they are not insured against the defeat of the tool and other sucking insects, which are carriers of viruses from other plants (vegetables, herbs, rootpodes, etc.).
Fortunately, not all peonies are sharply reacting to viruses in contrast to gladiols or tulips. Most of the old varieties are quite resistant to diseases and do not show any signs of infection at all, which will not say about many early-driving terry hybrids - they quickly face and often die. However, if you protect and take measures to take a timely manner, you can cure even the most capricious variety.
The problem also consists in the fact that usually peonies suffer from some one pathogen, but from a mixed infection. For example, it can be a yellow bean mosaic virus, cucumber, scaffolding, daffississ, aspermia of tomato, clatchiness of cloves, etc. Very often, viruses affecting peonies accompanies tobacco breeding virus, which was previously called ring spot virus. Symptoms will be noticeable even inexperienced gardeners - ring marks and strips of different shapes and colors will appear between the leaf veins, ranging from yellowish green, finishing bright yellow. When these elements merge, "marble" pattern is formed on the leaves.
Common fungal peonies:
- Gray rot - Young peonies seedlings in the spring are covered with brownish spots and boot in these places. You can clearly see the black dots of the fungny. The stalks begin to be frown, after which they break and fall. The disease is developing rapidly, especially in cool rainy weather and in areas with clay soils, where water is stuffed. The greatest hybrid varieties are most susceptible.

- Rust - Symptoms can be seen after the dissolution of buds. These are brownish, brown and red spots on the outside of the leaves, and on the reverse side appear "pads" with mushroom disputes inside. The disease extends very quickly and in just a week can settle on all nearby plants, especially in warm and wet weather.

- Buuray spotty - infection occurs at the beginning of summer and manifests itself in the form of large brown and dark burgundy spots, gradually increasing in size and capable of float all the sheet plate. It seems that the leaves are burned. In cloudy weather on the back of the leaves, the ash colors are formed - this is a sign of the spioning of the mushroom. In some cases, the disease can hit buds and stems.

- Root rot - Mushrooms are striking roots, stems and cuttings, leading to the death of the plant. You can detect the disease when transplanting or separated a bush. The rhizomes of patients with peonies become brown and soft, and with high humidity of the soil appears as a ash or pinkish flare. The increased acidity of the soil to the abundance of moisture contributes to the spread of the disease.
Unfortunately, drugs from viruses have not yet come up with, so if you have noticed an infected plant, burn it. If the "patient" is a very rare variety, squeeze it away from the main flower garden, divide into small parts with 1-2 kidneys and choose the strongest sprouts, leaving only healthy roots. Transplant the peony every 2-3 years, carrying out the clone selection of the most healthy sites, and over time it can free themselves from viruses.
Useful advice: Squake peonies as far as possible from strawberries, potatoes, raspberry bushes, tomatoes and cucumbers. Thus, you reduce the probability of propagation of pests sucking insects.
An organic agrotechnology is played a huge role in the prevention of diseases. Try not to use fresh manure and grass for peonies, but to mulch an exceptionally old compost. Mineral fertilizers put locally and do not overflow the plants with nitrogen.


























 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...