Often, the task is often placed in front of the homeowner, how to plan heating and hot water in your home. Implementation of the heating system with solid fuel, gas and electricity carries certain difficulties and costs. To organize heat exchange and effective energy saving with the help of self-promoted energy sources (natural soil, water and air resources), heating is used by the heat pump.
Content
Varieties of thermal pumps
There are thermal pumps of the following types:
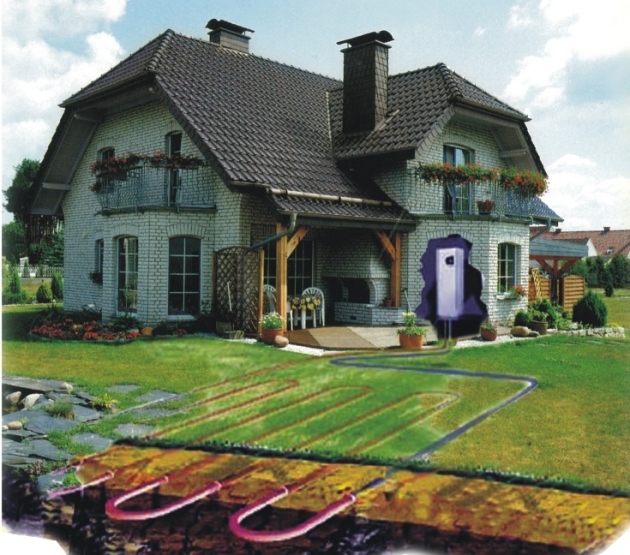
- earth and water - using water or brine, as well as using a soil probe. The ground pump can be installed using the probe on the plot of a small area, or using a collector laid under the level of ground freezing at a large land plot. Such a heat pump is suitable for heating and heating the water of buildings of various types, does not require complex maintenance and durable;
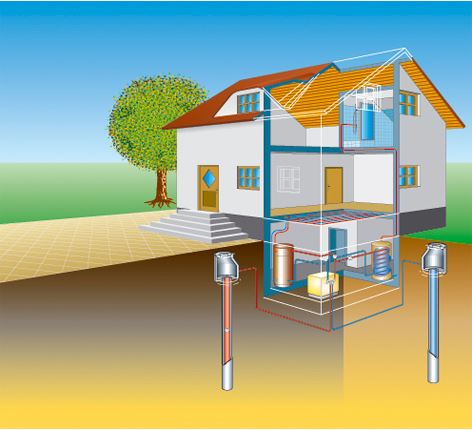
- water and water - this system is open, used primer or lake, river, sea (with fixing the hose at the bottom of the reservoir). Effectively use of the heat pump for home heating, passive air cooling, as well as for organizing water heating;

- air and air - on the principle of air heat transfer. The air thermal pump gets heat from the outside of the building through the evaporative unit. Such a system is used only to heat the air indoor;

- water and air - using a soil probe or well, as well as air. This system works on the air conditioner principle - with the difference that heating is not air, but water as a coolant. It is used for heating a country house with a thermal pump, as well as for organizing hot heat supply.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the advantages of heating at home, the thermal pump can be called:
- energy saving and efficiency - reduced heating costs, heat pumps supply energy to maintain a comfortable temperature and water heating with minimum power consumption from the source of electricity;
- universality of use - this system pumps heat from a practically inexhaustible energy reservoir - natural environment. The heat pump can be used both in industrial facilities and in private buildings. Compatible with any circulating heating system, can be used both for heating and air conditioning. The heat pump can act in the steelectricel mode - the heat exchanger, which will be used in the summer of excess heat to heat water;
- ease of operation - the heat pump does not need a specially equipped ventilation system, protected from power interruptions, steadily and reliably operates offline, does not require special maintenance. Can be used in the bivalent schemes of heating systems - together with a gas boiler or an electric concrete;
- environmental friendliness - this system is safe for human health, moisturizes air, does not highlight into heated premises of potential allergens, as well as in the environment of harmful emissions, combustion products;
- application safety - this system is absolutely explosive and fireproof, as the burning of fuel, gases and toxic mixtures are absent. When the system is stopped, there is no possibility of freezing of fluid and the subsequent failure of the pump.

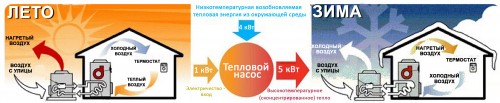
According to the reviews of thermal pumps, their use is effective in low temperatures mode - for example, for water heating. In the heat, it is possible to use the operation of the heat pump to cool the room - the heat is transmitted to the refrigerant and is derived from the house through the heat exchanger outward. In the process of heat exchange, the system consumes electrical energy much more efficient than traditional electrocotes.
The disadvantages of this system include:
- a rather high price of the heat pump relative to traditional heating schemes. For example, compared with the installation of a gas or electric boiler, a geothermal pump (in which the Earth acts as a source of thermal energy) will cost much more expensive, the costs will pay off after a long time;
- the heat pump will take the same area in the boiler room as a gas boiler. Additionally, for vertical probes at the rate of 1 kW of thermal power, about 25 m will be required. 2 square of the site for placement, for horizontal - up to 250 m 2. To accommodate in water, access to the water and some of its area;
- the heat pump refers to high-precision equipment that requires connecting to a three-phase network. It should be noted that the launch of the compressor is characterized by a high starter (possibly, a smooth starter will be required);
- the heating system with a heat pump, as a rule, is equipped with a spiral compressor, characterized by a significant level of noise - despite the use of sound insulation materials. Thus, it may be necessary for the equipment of an individual boiler room, and for high-power models from 40 kW - equipment with its special sound insulation materials;
- well drilling implies the re-landscaping of the adjacent land. In addition, it may be necessary to coordinate drilling work.
Device and principle of action of the heat pump
The thermal pump invented in the nineteenth century English physicist, later his Austrian engineer has improved him. In the 40s of the twentieth century, they invented how to use heat released during the freezer for heating at home and water heating. In the future, the technology of heating with the help of the heat pump was distributed in the 70s - due to the development of the global trend of energy saving. Simply put, the heat pump is functioning according to the scheme resembling the operation of the refrigerator. In the refrigeration unit, heat from food heats the refrigerant circulating over the pipes, in the heat pump system, on the contrary, it is transferred to the house accumulated in soil, water, air or deep bowls heat.
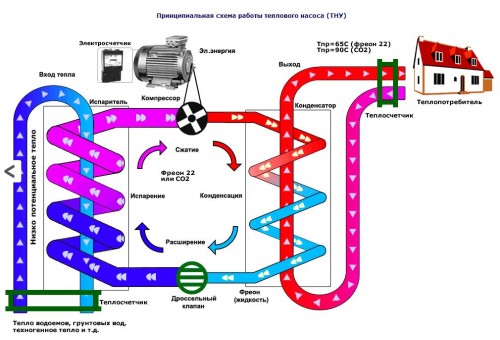
The main components of the thermal pump are:
- evaporator;
- capacitor;
- lowering pressure throttle valve;
- increased pressure compressor feeding from the mains.
These components of the heat pump are associated with a single closed system using a pipeline, according to which the liquid circulates in one part of the cycle into another gas. The boiling point of the refrigerant is about 40 ° C, so it can be used with a low-temperature thermal source, the boiling point changes with pressure change.
The heating system using a heat pump is cyclically as follows:
- the collector enters the fluid (alcohol or hydrochloric solution, the glycol mixture), absorbing heat and delivering it to the pump;
- on the evaporator, the energy is transmitted to the refrigerant - boiling and turning into gas, it takes the heat supplied by the collector from the environment;
- the gas entering the compressor is compressed - and, heating, pushes into the condenser;
- the compressor acts as a heat transfer film - heats the heat carrier of the heating system in the house, while the refrigerant goes back to the liquid state and is sent to the collector.

Power of heat pump
The necessary thermal pump performance is recommended to count after the insulation of windows, as well as walls and roofs, based on the existing requirements of the building. It is possible to conduct an indicative calculation, based on the area of \u200b\u200bheated premises and the total consumption of hot water. It should be borne in mind that in medium latitudes, the heat pump usually covers about 60% of the annual treatment of heat energy for heating, as well as hot water supply.















 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...