How to grow a lavender in the Urals, given the complex climatic conditions of the region and the southern origin of culture? It turns out there is nothing impossible. It is enough to choose the variety of lavender and explore the features of planting and leaving the plant in the cold climatic zone.
Content |
Then, unpretentious, hardy and magnificent plant, Lavender, will be able to delight the abundance of gently lilac inflorescences not only in southern countries, but also in the harsh Urals. In this article - all the peculiarities of growing lavender in the Urals.
Lavender in the Urals, description of the plant
- Lavender - the generation of the family of Casnotkov, is an evergreen long-term semi-stabiliar. The average life expectancy of the culture is about 10 years.

- The homeland lavender is considered the Mediterranean coast.
- The height of the plant on average reaches 50-80 cm. The root in perennial is thick, powerful, reaching up to 4 m in length.
- Bucket lavender consists of numerous branches, it looks compact and neat. SIZY Tint Plant acquires due to narrow and pubescent grayish leaves.

- The truly transformed plant in the summer, during flowering period. Lilavial-lilac small flowers collected in the inflorescence of the spikes, densely seated throughout the bush. Currently, varieties with white, blue and pink lavender flowers are also displayed.

- The name of this fragrant ether solid plant is translated from Latin, as "wash". This is explained by the initial use of grass, still the Romans, as an aromatic additive when bathing. Currently, Lavender is a widely known decorative plant. A, pronounced, the smell of perennial allows you to actively use it in the perfume and cosmetic industry.
- Lavender, a light-affilome and drought-resistant plant, can be easily raised in warm southern regions.
- Given the unpretentiousness and endurance of the plant, it is successfully cultivated in more severe conditions, for example, in the Urals.
- Then, the flowers are grown in pots or in the open ground, but, observing certain rules of care and competently selecting frost-resistant varieties.
Types and varieties of lavender grown in the Urals
The geography and relief of the region largely identified the climate of the Urals. Mountains, the main part of the territory of the Urals, denote dominating severe continental climatic conditions there. Cold winters, strong winds and low temperatures - the main "satellites" of the region of the middle strip of Russia.
Although there are significant differences within one region: for example, the difference between the natural conditions of the southern and northern parts of the Urals. The cultivation of lavender in the southern part of the Urals is preferable, given the softer and humid climate. The South Urals is a favorable natural zone for growing many plant crops. Other parts of the Urals require significant endurance and adaptation of plants disembodied in harsh climatic conditions.
Around the world, more than 25 types of lavender are cultivated, although only some of them became truly popular.
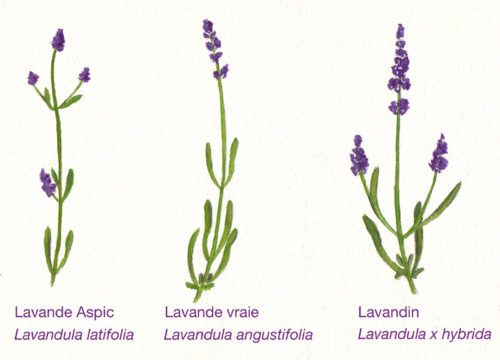
The cultivation of lavender in the Urals requires the presence of high frost and vitality in the plant. Such characteristics are responsible for the known species - lavender narrow-walled or English ( Lavándula Angustifólia.). The plant grows perfectly in the Urals and in Siberia, withstanding frosts up to - 35 ° C (with shelter).
The view refers to the climatic zone of plants number 4.
The perennial reaches a height of about 60-70 cm. It has a view of a spherical semi-stabiliar with numerous shoots, weathered at the bottom. Narrow leaves, sizo-silver shades, covered with easy-to-wear. Fragrant inflorescences of lipid flowers, collected in the ears, have purple-lilac shades. Blossom comes in June-July, less often - in August.
Winter-hardy and unpretentious species served as the basis for the selection of various varieties that are successfully grown in the Urals.
- Munstead grade is distinguished by the saturation of blue shades of inflorescences and low (up to 40 cm) with a bustard sustainable to strong winds.
- Hidcote series varieties are very beautiful and attractive. Hidcote VLU is characterized by bright purple flowers and shortness of the compact half-ward. Hidcote Giant has dense, but higher lavender bushes.
- The ALBA variety is highlighted by white inflorescences and medium (up to 50 cm) sizes, a bush.
- Rosea variety is represented by gentle pink inflorescences.
- BEECHWOOD BLUE variety has tender lilac blue inflorescences.
In addition to the lavender narrow-walled, planting in open ground, other, thermal-loving species, lavender can be grown in the Urals. But only under one condition - as a room potted culture or as a homing during the period of warm season.
Lavender reproduction in the Urals
Lavender is perfectly multiplied as vegetative (tanks, cuttings, bush division), and by a generative way, i.e. Seeds.
In the conditions of the cold climate of the Urals, the most optimal method of reproduction is considered a seed method.
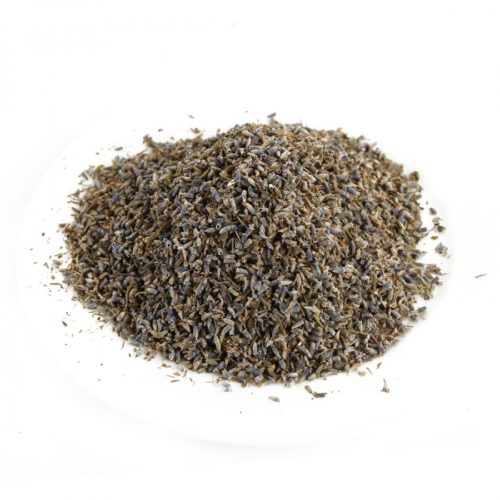

- Lavender seeds can be stored in a dry cool place for several years, while they fully retain the germination. A bag with seeds should be hermetically closed.
- Before sowing is carried out stratification, i.e. Charging seeds. Seed hardening technology is especially important for cold climatic zones. For stratification, the package with seeds in February or March is placed in the refrigerator. In April, tempered in this way, the sowing material is ready to evounce in open ground. Another stratification method consists in mixing seeds with moistened sand, after which the package or container is also placed in a cold place.
- Seed seeds are also practiced, followed by a transplant in open soil. Seeds exiled in February-March, at a temperature of about 20 ° C quickly germinate. The depth of seed seeds is not more than 3 mm. At the stage of the second sheet, shoots dive. In May, seedlings are planted at a permanent place. Gardeners of the Urals noted that the lavender grown in such a way, less worn, rather than when sowing directly into the open ground.

- The autumn sowing lavender is also practiced, in September-October, before the onset of frosts. The percentage of germination is significantly lower than in the conditions of spring landing. In winter, it is important to fall asleep this section with a thick layer of snow.
- In the self-sewing plants, seeds, as a rule, do not germinate, dilding in conditions of harsh cold winter.
- With a seed breeding method, bloom comes to 2-3rd year.
- Many flower products prefer to grow lavender in vases or pots, exposing them to the street. Upon the onset of the first cold, they are immediately entered into a warm room for wintering.

Lavender in the Urals, Agrotechnical landing
- Choosing a place to land a perennial lavender, it is better to stay at the maximum sunny, windless and warmed place. The plant is well evolving on dry elevated places or in the foothills.
- The soil will fit almost any, better sandy-clay. It may even be gravel or non-fermented soil. It is optimally provided for the plant well drained, moderately nutritious, light soil, with neutral acidity and deep groundwater. With increased soil acidity, it is additionally made lime.
- Sowing seeds in open soil carry out shallow, about 4 mm, on top of a slightly sealing soil and watering a water area.
- If the lavender is planted to plant in room pots, you should prepare so far from the delicate earth with the addition of sand and humus. It is important to provide for the presence of a drainage layer of pebbles, gravel or broken sharps in the container. Lavender is a light-affilome plant, so the pot is placed in a warm and bright, affordable sunshine, place. If the flower gets light less than 6 hours per day, a fluorescent lamp will be required.

Lavender in the Urals, care
Neutual to special care conditions, lavender, grown in the Urals, still needs certain agrotechnical techniques.
First of all, it is essential to the timely trimming and shelter of lavender for the winter period. Such procedures are extremely important for the cultures of the cold climatic belt of the middle strip of Russia.
The rest of the plant concern is reduced to traditional watering activities, feeding and pest control.
Watering:
- Lavender, drought-resistant plant preferring moderate watering.
- Wateringit is carried out as the soil drying.
- Undesirable will be permanent movement or fever Soil. In such conditions it is important to ensure good soil drainage. Otherwise, the root of the plant can be started, and a bush to die.
- Lack of moisture Reduces the abundance of perennial flowering. After flowering, watering stops.
- If Lavender grows on the slopes, you can equip at the foot of the bushes, watering holes. Such a simple device will help detain moisture.
Mulching and loosening:
- Do not mulch Soil for lavender. Culture does not need a constant wet microclimate. In addition, the mulch prevents the aeration of the root system of perennial.
- When use of decorative mulching swelling, It is necessary to leave an open sphere of soil.
- To improve the breathing of the roots, 1-2 times throughout the growing season are carried out the soil loosening.
- Mulching with a thin layer (5 cm) peat or loose compost in pre-time.
Feeding:
- Lavender - not demanding, To additional feeding, culture. Nevertheless, fertilizer will be favorable at its development.
- The feeder is carried out twice: In the spring, at the beginning of the vegetation, and in the summer, before the blooming of the semi-stabiliar.
- From fertilizers, spring Most often used urea solution (0.5 tbsp. by 5 l. water). This is a portion for one adult bush plants. During this period, organic feeders are used, which are not deeply close in the soil around the plant.
- Summerlavender fertilizes the complex organicerial fertilizer "Agrikola" in proportions, according to the instructions of the drug. You can also use a solution of organic fertilizer "Ross Universal".
- Lavender reacts well to potassium-containing fertilizers. Nitrogen fertilizers or manure are less desirable, because Promotes the growing green mass, which negatively affects the flowering of lavender.
Trimming:
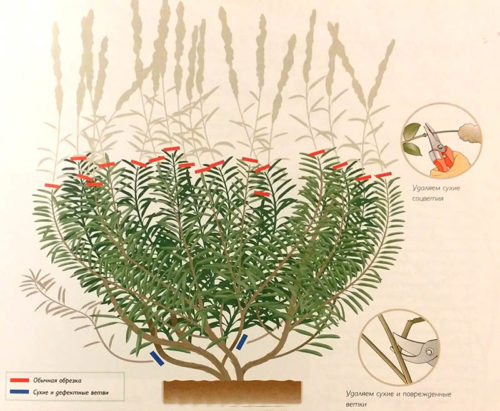
- To preserve the plant during the period of harsh winter in the Urals, Lavender in the fall do not cut. Numerous stems do not allow the plant to freeze in winter, protecting the same and the root system of perennial.
- In this climatic zone, Lavender cut off in the spring Forming neat compact bushes and in summer, immediately after flowering. In the spring, they remove all the dry, damaged stems, leaving 5-6 young green escapes.
- It is impossible to cut a bush lavender very much - to the widespread stemsThis will cause the death of the plant.
- Small trimming helps shape Kostikov lavender I. rejuvenates plant.
Fighting pests and diseases:
- Lavender practically not subject to pest attack. In this she helps fragrant essential oils that scare insects.
- From pests, you can meet in Lavender rainbow Zhukaessaying foliage. For extermination, it should be collected from plants manually.
- Sometimes, white foam appears on the plant, which, in fact, does not harm the plant, but spoils an external aesthetic appearance. it pennyni larvaeIn defective purposes covered with a layer of foam. It is very easy to fight with them - it is enough to simply wash off their jet of water.
- Occasionally, plant sick sulfur. The affected parts of the plant are removed and burned.
Winter shelter:
- This procedure is mandatory When growing lavender in cold areas of Russia, including in the Urals.
- Before the onset of cold plant is covered with remedies: burlap, agrofluorine. You can additionally insulate the bushes with the help of branches of coniferous trees.
- Do not cover the bushes with fallen leaves or compost - This can lead to a planting of the plant.
Landing and lavender care in the Urals, reviews
- The flower of the Urals mark the main danger for the lavender in the cold climatic zone, not in severe frosts, and in frequent sparing plants. In order to prevent this, it is important to ensure a moderate watering of culture, without moisture.
- Many gardeners practice growing lavender in decorative vasesthat in front of the onset of cold weather are entering a warm room. Flowers are preparing for the rest period, placing them in a cool place and significantly reducing watering.

- Growing lavender in the Urals, gardeners celebrate the most optimal method of breeding - Seed. When dividing the bush to pieces or reproduction with tanks, cuttings, lavender often does not give massive positive results. Does not like a plant and transfers to another place.
- Experienced flowerflowers recommend regularly cut faded inflorescences Lavender, which significantly prolongs the period of flowering perennial.

Using lavender
- Lavender is beautiful medonosom, attracting a large number of bees with its subtle aroma.
- Perennially recognized in many countries one of the best decorative plants When designing diverse landscapes: Park zones, gardens, alleys or borders. Mass landings of evergreen semi-stares fascinate with their magnificence and bright shades during flowering.

- V cosmetology and perfumery The fragrant lavender oil is widely used.
- Culture and in medicine As a soothing and toning agent. Thin fragrance of lavender helps reduce headaches, migraine.

- In cooking Lavender is used by an unusual spicy taste.
- At home, the lavender twigs have been considered reliable tool from moth. They were spacked in the closet, giving the pleasant thin flower flavor to the same clothes.

Summing up, it is necessary to clearly designate the difference in the cultivation of lavender in southern regions and cold climatic zones. Knowing the peculiarities of growing lavender in the middle lane of Russia, it is easy to ensure the prosperity and development of culture in such non-constant for plants, climatic conditions.
- First, for planting in the northern regions, it is necessary to choose frost-resistant varieties and types of lavender.
- Secondly, the right choice of place when planting culture will be provided in the future, its optimal development and abundant flowering.
- Thirdly, the knowledge of the lavender care features in the Urals will be a guarantee of a favorable wintering of perennial and its further development on the site.



















 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...