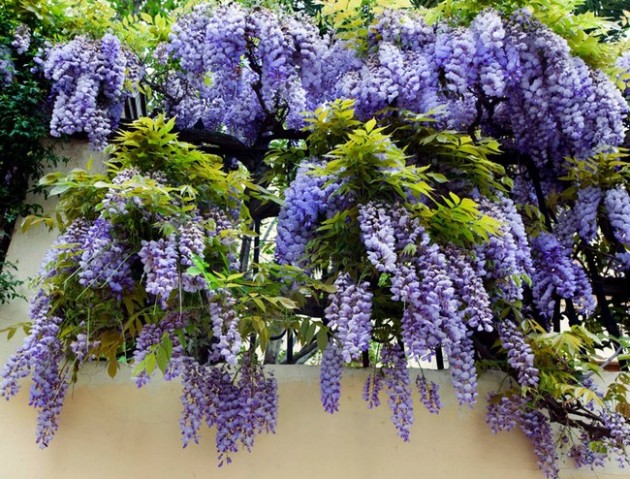
Wisteria (Visteria) Blue Moon is a beautiful perennial liana, striking with its magnificence. In sunny weather, her lavender-blue, like a fragrant waterfall, borders create a cool effect. And with the arrival of twilight, the inflorescences fascinate with lunar silver radiance. Such an incredible spectacle was the cause of the gentle name of this beauty - a blue moon or blue moon. This plant is happy every gardener, because his decorative is able to decorate any garden of the garden - hedge, Altanka, the wall. How to grow this glinate, and what difficulties may arise - the topic of this article.
Glicinia Blue Moon, description
Wisteriamacrostachya Blue Moon Macrotache (Wisteriamacrostachya Blue Moon) is a tree-shaped representative of deciduous lian, which are combined into the bean family. Favorable growth environment - wet subtropics. Therefore, in nature, wisteria is mainly found in some regions of the United States, China, Japan.
After the Canadian Blue Moon came to Russia, the attempts to grow in the harsh Russian climate were unsuccessful. But perseverance won, and wisteria was gradually acclimatized. Now it is often used in landscape design. It can be met in the south of Russia, in the Crimea, as well as the Northern Black Sea region. Also, glitching is successfully grown as a room bonsai.
Characteristics of Glycine Blue Moon:
- The plant develops rapidly and goes, the height of its shoots may exceed 6 m. Rhizer wisteria is durable, germinating deep into the soil.
- On bending shoots, graceful borders are formed by unusual colors - heavenly, pink-purple, violet, ultramarine-lavender color with yellowish necks. Freakty lengths up to 30 cm (depends on cultivation conditions).
- In comfortable conditions, glinate can be pulled out to 14-30 m in height. Its dumped shoots are decorated with a dark green color foliage. Glossy leaves, their structure is unpaired. Each sheet grows up to 27-30 cm and contains 8-13 leaves.
- Flowering falls on April-September. After its end, brown fruits enclosed in pods are formed.
- Glycine Moon's grade is considered frost-resistant and survives at -40⁰.
Glycine Blue Moon, breeding features
Glycine Blue Moon multiplies with different methods. More often uses airplane and reproduction by air chains. The seed method is less popular because it is rare to preserve varietal features.
Glicinia reproduction Blue Moon stalling
Shining is the optimal variant of the reproduction of Liana. With the help of Chenkov, you can successfully get a new seedling, which will retain the features of this species.
Glitenia reproduction rules:
- The billet of shoots begins in the spring.
- Choose and cut off one-year escape.
- In the middle of escape make a shallow oblique section.
- Escape planted into the nutritional soil to the place of the feet.
- At the end of September, the root escape is planted at a permanent place.
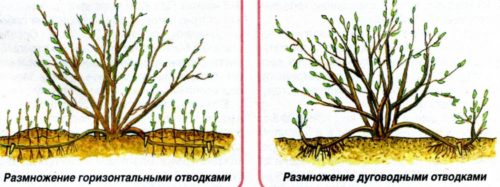
Glicinia reproduction Blue Moon
Liana willingly multiply by rooting of the messengers:
- The rooting is carried out in October-November, when Liana dropped the foliage.
- Lower shoots gently tilted and cheerfully cheer.
- About the root takes about the year.
- The shoots are checked, and if they have already acquired roots, they are separated and transplant.
Seed method of breeding Glycine Blue Moon
- If there is a desire to risk and grow liano from seeds, you need to start work in December (for the cultivation of seedlings) or in March (in open ground).
- For sowing seeds use flat containers filled with special soil (leaf land, sand, nervous land in a 2: 1: 1 ratio).
- Seeds are laid in the wet soil (they are large and similar to beans), they do not close them, but simply they are covered with small crusts or sand.
- A greenhouse is constructed from above with simple glass or film material.
- Then the pot with seeds leave in the dark room for 10-15 days.
- After the appearance of sprouts, the pot is transferred to light.
- When seedling in the greenhouse conditions is strengthened, it is planted for a permanent place.
Advice! Success will be possible only if seeds are sowing from the plant, which grows in your region.
Wiccine Methods of Blue Moon
Lianu is grown in two ways - in a container or in open ground, which depends on its sustainability to the existing climatic conditions.
Growing in the container:
- If the plant does badly tolerate freezing, it is transferred to a large container. Its volume should be at least 40 liters.
- With the arrival of winter, the container with Liana is cleaned into a warm room. Throughout this period, watering and feeding are reduced to a minimum.
- In anticipation of spring, watering is resumed - 3-4 times a week.
- When the risk of compensation of frosts passes, the plant is put on the street.
- A significant lack of such a method is the complexity of leaving due to impressive weight of Liana.
Growing outdoor:
- Only a young seedling of Glycinia Blue Moon is being landed. You can buy it in nurseries specializing in the cultivation of Lian, or grow from seeds.
- Glicinia will bloom only 5 years after landing or later.
- If the wisteria is grown from the seed, it may not save its varietal features, but will be very resistant to weather.
Glicinia Blue Moon, landing and care
An important point in the cultivation of wisteria is the choice of an ideal landing site and the process of its rooting. If there were no problems with this, further care for the Glyciny of Blue Moon is very simple.
Conditions for growing Glycine Blue Moon
The puff of flowering and the rue of the glotern of wisteria of Blue Moon depends on the place of its cultivation:
- Climatic zone. Wisteria Frost-resistant Blue Moon willingly leaving in any region. Correct care allows wisteria to be calmly winter in conditions of up to -40⁰, so it is available for growing in the open ground.
- Plot.. Blue Moon responds well to scattered sunlight, while straight rays or strong shading adversely affect flowering. Therefore, you need to choose a plot with southern orientation, and necessarily with a transparent hedge. Required sunny day - more than 12 hours.
- The soil. The composition of the soil for Liana is not fundamental, the main thing is to ensure the laughter of the soil so that there is good access of air and moisture to the rhizomet. An excellent choice for Blue Moon - sandstones and light loams.
On a note! If the glycium of Blue Moon is growing in limestone, its foliage becomes fading, and liana loses his decorativeness.
Features of the landing of wisteria Blue Moon
So that wisteria successfully rooted and continued its growing up in a new place, be sure to prepare the pit for landing:
- Choosing a landing space, the growth intensity of wisteria is taken into account. After 2-3 years, a small seedling is greatly growing and wisteria requires a lot of space.
- 3-6 months before planting a seedling, a mixture of mineral and organic fertilizers contribute to the pit. If it did not work out, the combined feeding is necessarily introduced in the process of planting the Glycine Moon.
- At the bottom of the pit, the clamzite or broken brick is always poured. A sufficient drainage allows you to protect the rhizome from the convergence.
Garden care for Glyciny Blue Moon
Caring for glycini is simple: you need to regularly water and feed the Lian, if you wish, carry out trimming, be sure to protect against pests.
Watering Glycine Blue Moon
Watering Liana has several features:
- The overwhelming of wisteria leads to diseases and deterioration of its appearance.
- Moisturizing in the period of active vegetation is carried out twice a week.
- Abundant watering is carried out only during flowering. As a rule, Liana watered daily.
- Starting from September, watering slowly reduce and completely stop until December.
Advice! To cut watering soil and not harm this rhizuch, it is better to quickly spray the leaves early in the morning and after sunset.
Undercalinking Glycine Blue Moon
The question of fertilizing wisteria is very important. Feeding Lian, it is important not to rearrange, since excess minerals are more harmful for it than the deficit. But this does not mean that the feeding should be refused. They are extremely necessary for lush flowering and beautiful color of greenery.
- Use comprehensive fertilizers that are bred by the instructions. As a rule, take 20 g fertilizers on the water bucket. There is enough such quantity on a square meter of soil.
- Beneficiously affects the growth of Glicinia. 100 g of chalk and 10 liters of water are mixed for the solution.
- During flowering, mineral mixtures for flowering crops or compost are used.
Glicinia Transplant Blue Moon
Transplanting Glycinia Blue Moon, according to gardeners, is a controversial issue. Some claim that it is impossible to transplant the plant, others assure that a young seedling in need can be transplanted to a new place.
It should be noted that it is possible to risk with a transplant only if the wisteria is less than one year. But it does not guarantee that it is rooted. Wisteria can dive for a long time to rest or dry out.
If the transplant of Wisteria is a forced step, it is important to comply with these rules:
- Before boarding, shooting great shoots.
- A new landing place is carefully prepared for all the rules.
- Rhizome wisteria digs together with a large land of land.
- Carefully transfer to a new place are immersed in the pit.
- Fall asleep soil and watered.
Blue Moon Flowering
Abundant bright blossom of wisteria occurs from May to June. And in the warmth climate, Wisteria has a second bloom wave - from the end of June to autumn. In the southern regions sometimes there is a third period of flowering, which starts in October.
So that new buds were large, with a beautiful saturated color, it is important to overtake all the faded inflorescences. Do not forget at this stage and about constant feeding.
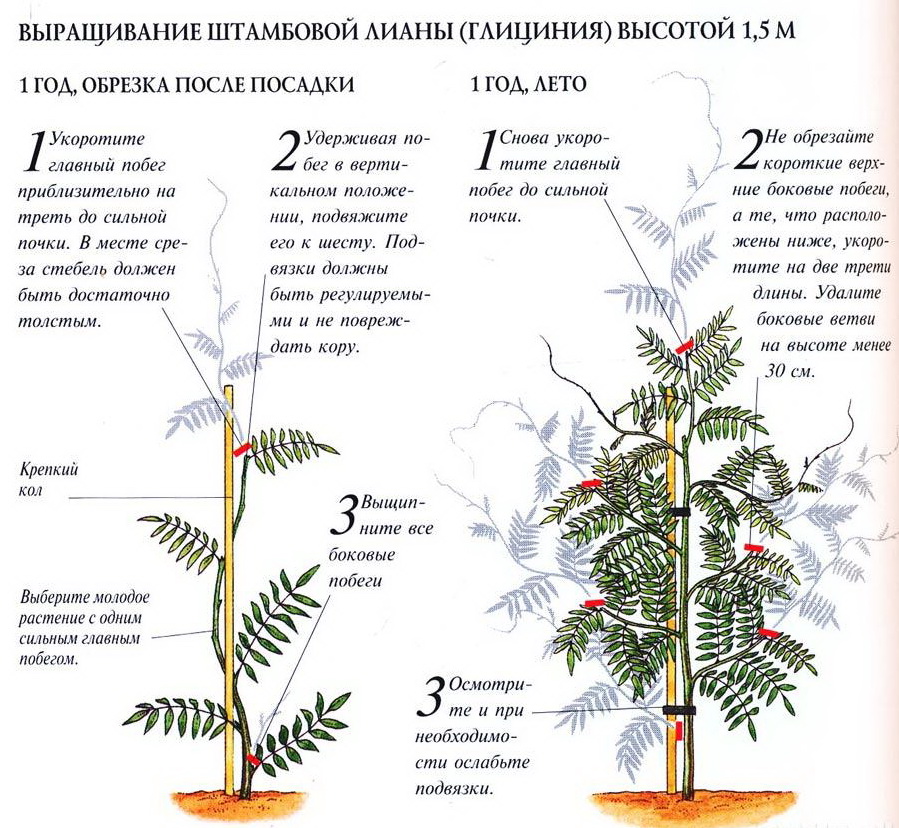
Glycine Blue Moon, Pruning and Formation
This kind of Lian needs pruning, because if it does not limit her growth, it can achieve incredible sizes. In nature, wisteria often grows up to 30 m in height and up to 15 width.
- In the first year, the young seedlings of wisteria, which were planted in early spring, cut off several roasting shoots that quickly reaching in growth. If side branches appear, they are also shortened.
- If the liana is grown on a hat and its purpose - cover the structure, for example, a wall or a high hedge, during the landing pinch the main escape at the level of 90 cm above the ground. This contributes to the formation of new kidneys, and then young side shoots are sent to the desired side: the top is fixed vertically, and the remaining at an angle of 45⁰.
- For the second year after winter, the main stem cut up to 80 cm from the top side escape. Then the rest of the side shoots are hosted horizontally and cut off to a third, which is stimulating the formation of lateral kidneys. Such trimming is carried out every year.
- Every year, in August, the extra side sprigs of the first and second row to 20 cm from the main stem are cut. This is necessary for the formation of short coloring. Also remove young root shoots.
- Adult wisteria after the residual formation of the skeleton, in August, is eliminated from seasonal growths (they can reach 2-4 m). They are cut up to 15 cm from the main escape, and in the winter once again shorten up to 8 cm from the base.
- To stimulate the flowering of glinate blue moon, every two weeks the gains are shortened to 12-17 cm from the base. This is done throughout the summer.
Glycine Blue Moon, Diseases and Pest
Frequent diseases and damage pests are not typical for wisteria. Among possible problems can be called:
- The clover tick is manifested by the bronze color of the leaves and is perfectly treated by any acaricide.
- Caterpillars - insects actively eat leaves and completely destroy greens without treatment, making it like a sieve. For prophylaxis, Lian needs to spray with biological preparations.
- Green TLA - insects suck out juice from leaves, reducing the decorativeness of wisteria. Insecticides are used to combat them.































 Start a discussion ...
Start a discussion ...